×
Il semble que vous utilisiez une version obsolète de internet explorer. Internet explorer n'est plus supporté par Microsoft depuis fin 2015. Nous vous invitons à utiliser un navigateur plus récent tel que Firefox, Google Chrome ou Microsoft Edge.
My Player placeholder

Devenez membre d'Incathlab et bénéficiez d'un accès complet !
Vous devez être membre pour accéder aux vidéos Incathlab sans limitation. Inscrivez vous gratuitement en moins d'une minute et accédez à tous les services Incathlab ! Vous avez aussi la possibilité de vous connecter directement avec votre compte facebook ou twitter en cliquant sur login en haut à droite du site.
Inscription Connexion
Inscription Connexion
This didactic procedure concerns a left side ilio-femoral chronic venous obstruction.
Educationnel objectives
- Plan a step-by-step ilio-femoral chronic venous obstruction procedure.
- Materials choice: guidewires, support catheters, balloons and dedicated stents.
- Learn different techniques to advance and manipulate guidewire through the occlusion.
- How to proceed to an optimal lesion preparation?
- Tips and tricks for a good positioning and implantation of the stents.
- Advantage and usefulness of IVUS to optimize the procedure?
- Importance of adjunctive pharmacotherapies?
Step-by-step procedure: Left internal carotid artery stenting
1) Access sites:
- Femoral access: Echo guided puncture at mid femoral vein (Sheath position: upstream to the lesion and avoid conflict between the sheath and the occlusion).
- 7 French sheath.
- First contrast injection to establish vein cartography with different collaterals.
- Anticoagulation.
2) Recanalization
- Park an angled stiff Terumo® RADIOFOCUS® wire 0.035” at the entry of the occlusion.
- Advance the wire through the occlusion: with a combination of torque and push movements with the support of a vertebral Glidecath® TERUMO®catheter 4Fr.
- Improve wire support after advancing through the lesion with a support catheter TrailBlazer™ catheter (after 2-3cm through the occlusion, improving the support to ensure enough pushability is extremely important).
- Check the trajectory of the wire in different orthogonal projections to be sure that the wire is in the vessel structure.
- Advancement with the loop wire technique in the common iliac vein (in case of failure to advance with the straight tip of the wire).
- Angio control to check the progression of the wire.
- Tips and tricks: To be sure that you are in the IVC: In the lateral projection, the wire or the catheter should be ventral to the vertebral body.
- After crossing the lesion exchange with a 0.035” Amplatz super stiff™ wire.
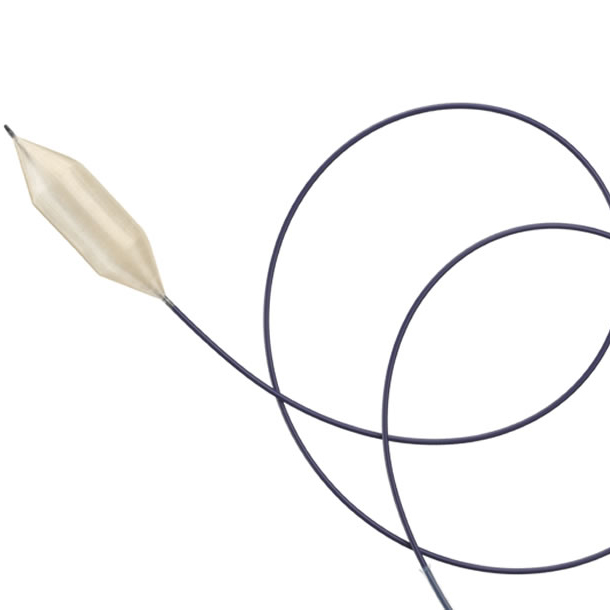
- Balloon pre-dilatation: Balloon pre-dilatation should be done from healthy -to- healthy part of the vein. A 7*60 mm Mustang® balloon used to dilate at the distal part of the occlusion (usually start at the proximal part of the occlusion unless facing difficulties to progress the balloon through the occlusion).
- Pre-dilatation with a 12*80mm Mustang® balloon.
- Stent diameter choice: external iliac vein: 12-14cm and common iliac vein: 14 -16 cm.
- IVUS control VISION PV 8.5 Fr 0.035”*90cm : Useful information from IVUS: results of the pre-dilatation, maximum point of the compression, length and diameter of the stent and landing zone of the stent (in addition to reducing contrast injection and radiation).
- Positioning the stent from healthy to health part of the vein.
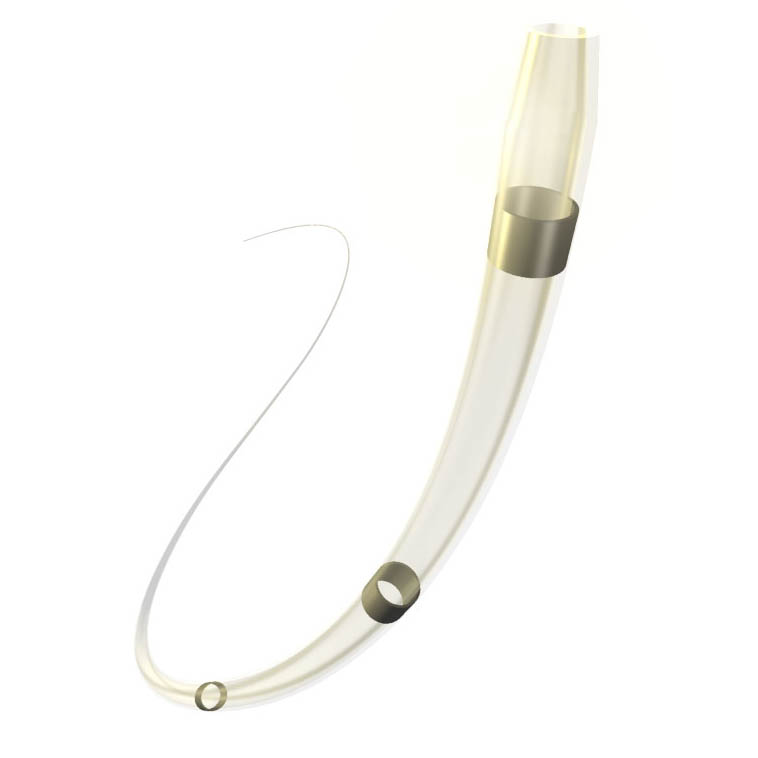
- Use a dedicated vein stent ATLAS GOLD® 14*60mm, ABRE™ STENT 14*150mm, ABRE™ stent 12-80mm (avoid overlapping at the level of the ligament area).
- Post dilation of the stent.
- IVUS control : stent opening geometry and control the landing zone.
- Final angio control: stent patency with no visualization of the deep femoral vein and the collaterals.
- Adjunctive therapies: Aggressive anticoagulation to maintain stent patency.
- Femoral access: Echo guided puncture at mid femoral vein (Sheath position: upstream to the lesion and avoid conflict between the sheath and the occlusion).
- 7 French sheath.
- First contrast injection to establish vein cartography with different collaterals.
- Anticoagulation.
Protocol
- Procedure time 125 min
- Exposure time 29.91 min
- Exposure 11463 mGy.cm²
- Contrast vomule :70ml Ioméron 350
Bibliography
-
Taha MAH, Busuttil A, Bootun R, Thabet BAH, Badawy AEH, Hassan HA, et al. A clinical guide to Deep venous stenting for chronic iliofemoral venous obstruction. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. mai 2021;S2213333X21002195.
-
Raju S. Best management options for chronic iliac vein stenosis and occlusion. J Vasc Surg. avr 2013;57(4):1163‑9.
-
Kölbel T, Lindh M, Åkesson M, Wassèlius J, Gottsäter A, Ivancev K. Chronic Iliac Vein Occlusion: Midterm Results of Endovascular Recanalization. J Endovasc Ther. août 2009;16(4):483‑91.
-
Rollo JC, Farley SM, Jimenez JC, Woo K, Lawrence PF, DeRubertis BG. Contemporary outcomes of elective iliocaval and infrainguinal venous intervention for post-thrombotic chronic venous occlusive disease. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. nov 2017;5(6):789‑99.
-
Seager MJ, Busuttil A, Dharmarajah B, Davies AH. Editor’s Choice – A Systematic Review of Endovenous Stenting in Chronic Venous Disease Secondary to Iliac Vein Obstruction. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. janv 2016;51(1):100‑20.
-
Wittens C, Davies AH, Bækgaard N, Broholm R, Cavezzi A, Chastanet S, et al. Editor’s Choice – Management of Chronic Venous Disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. juin 2015;49(6):678‑737.
-
Hood DB, Alexander JQ. Endovascular management of iliofemoral venous occlusive disease. Surg Clin North Am. oct 2004;84(5):1381‑96
-
Menez C, Rodiere M, Ghelfi J, Seinturier C, Martinelli T, Imbert B, et al. Endovascular Treatment of Post-thrombotic Venous Ilio-Femoral Occlusions: Prognostic Value of Venous Lesions Caudal to the Common Femoral Vein. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. août 2019;42(8):1117‑27.
-
Friedrich de Wolf MA, Arnoldussen CW, Grommes J, Hsien SG, Nelemans PJ, de Haan MW, et al. Minimally invasive treatment of chronic iliofemoral venous occlusive disease. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. avr 2013;1(2):146‑53.
-
Lichtenberg M, de Graaf R, Erbel C. Standards for recanalisation of chronic venous outflow obstructions. Vasa. 1 juin 2018;47(4):259‑66
-
Lichtenberg M, Stahlhoff S, Özkapi A, de Graaf R. Braided nitinol stent for chronic iliofemoral venous disease – the real-world BLUEFLOW registry. Vasa. sept 2021;50(5):372‑7.
-
Hans SS, Conrad MF, éditeurs. Vascular and endovascular complications: a practical approach. First edition. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2021.
-
Schleimer K, Barbati ME, Grommes J, Hoeft K, Toonder IM, Wittens CHA, et al. Update on diagnosis and treatment strategies in patients with post-thrombotic syndrome due to chronic venous obstruction and role of endovenous recanalization. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. juill 2019;7(4):592‑600.
-
Soosainathan A, Moore HM, Gohel MS, Davies AH. Scoring systems for the post-thrombotic syndrome. J Vasc Surg. janv 2013;57(1):254‑61.
-
Raju S, Neglén P. Percutaneous recanalization of total occlusions of the iliac vein. J Vasc Surg. août 2009;50(2):360‑8.
-
Majdalany B, Khaja M, Williams D. Intravascular Ultrasound-Guided Intervention for May–Thurner Syndrome. Semin Interv Radiol. juin 2017;34(02):201‑7.
-
Li Y, Zou Y, Wang S, Li J, Jing X, Yang M, et al. A Pilot Study of the FRAIL Scale on Predicting Outcomes in Chinese Elderly People With Type 2 Diabetes. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015;16(8):714.e7-714.e12.
-
Lichaa H, Lakhter V, Mohan J, Kerrigan J, Secemesky E. Intravascular Ultrasound Use for Iliac Vein Interventions. Curr Cardiovasc Imaging Rep. août 2021;14(8):8.
-
Marteslo JP, Makary MS, Khabiri H, Flanders V, Dowell JD. Intravascular Ultrasound for the Peripheral Vasculature—Current Applications and New Horizons. Ultrasound Med Biol. févr 2020;46(2):216‑24.
Date du tournage : 07/09/2020
Dernière mise à jour : 05/11/2021
Dernière mise à jour : 05/11/2021
Our Cases of the Month
The case of the month is a new way for our users to watch, learn, and share with incathlab. They can watch a video that highlights an innovative case and uses excellent pedagogical techniques, lear...
Partager
Participer à la discussion
Suggestions
November 2015
Honolulu : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 04h à 06h (GMT+1)
San Francisco : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 06h à 08h (GMT+1)
New York : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 09h à 11h (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 11h à 13h (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 14h à 16h (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 15h à 17h (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 16h à 18h (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 18h à 20h (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 21h à 23h (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 22h à 00h (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 23h à 01h (GMT+1)
Sydney : Jeudi 26 novembre 2015 de 00h à 02h (GMT+1)
Wellington : Jeudi 26 novembre 2015 de 02h à 04h (GMT+1)
San Francisco : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 06h à 08h (GMT+1)
New York : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 09h à 11h (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 11h à 13h (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 14h à 16h (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 15h à 17h (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 16h à 18h (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 18h à 20h (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 21h à 23h (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 22h à 00h (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Mercredi 25 novembre 2015 de 23h à 01h (GMT+1)
Sydney : Jeudi 26 novembre 2015 de 00h à 02h (GMT+1)
Wellington : Jeudi 26 novembre 2015 de 02h à 04h (GMT+1)
2nd live Websymposium on Venous Interventions
Learn and debate with the experts
Partager
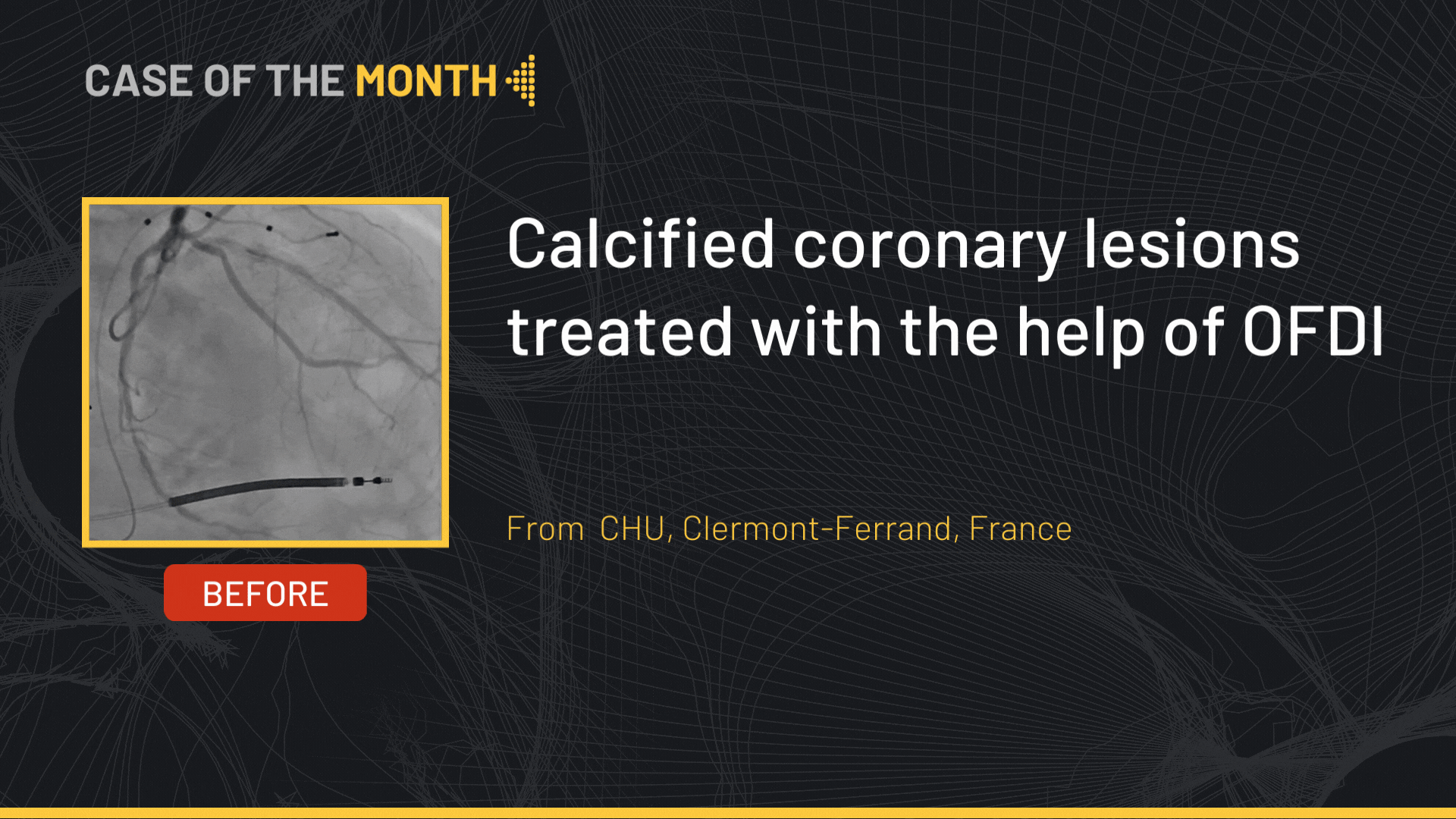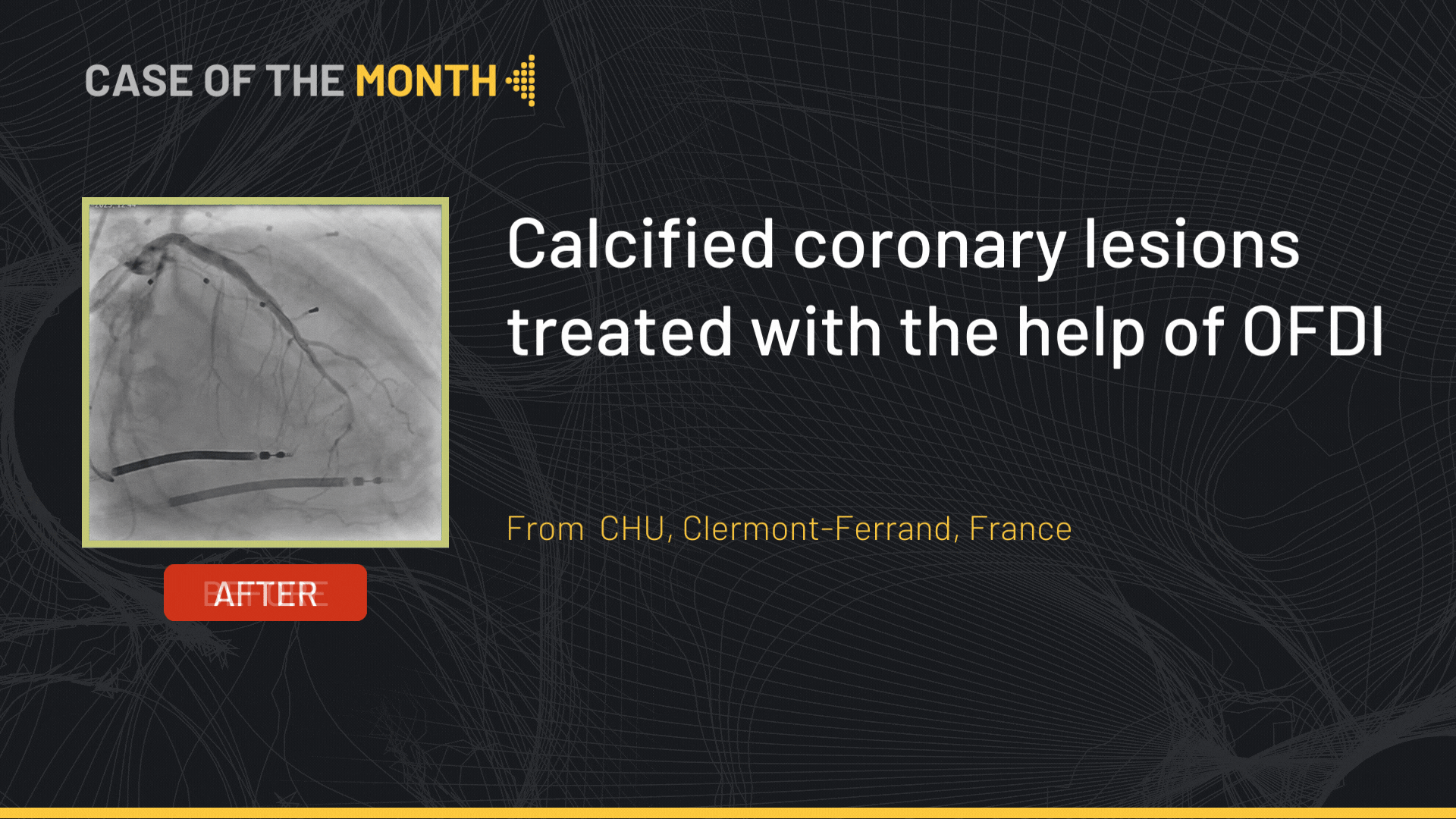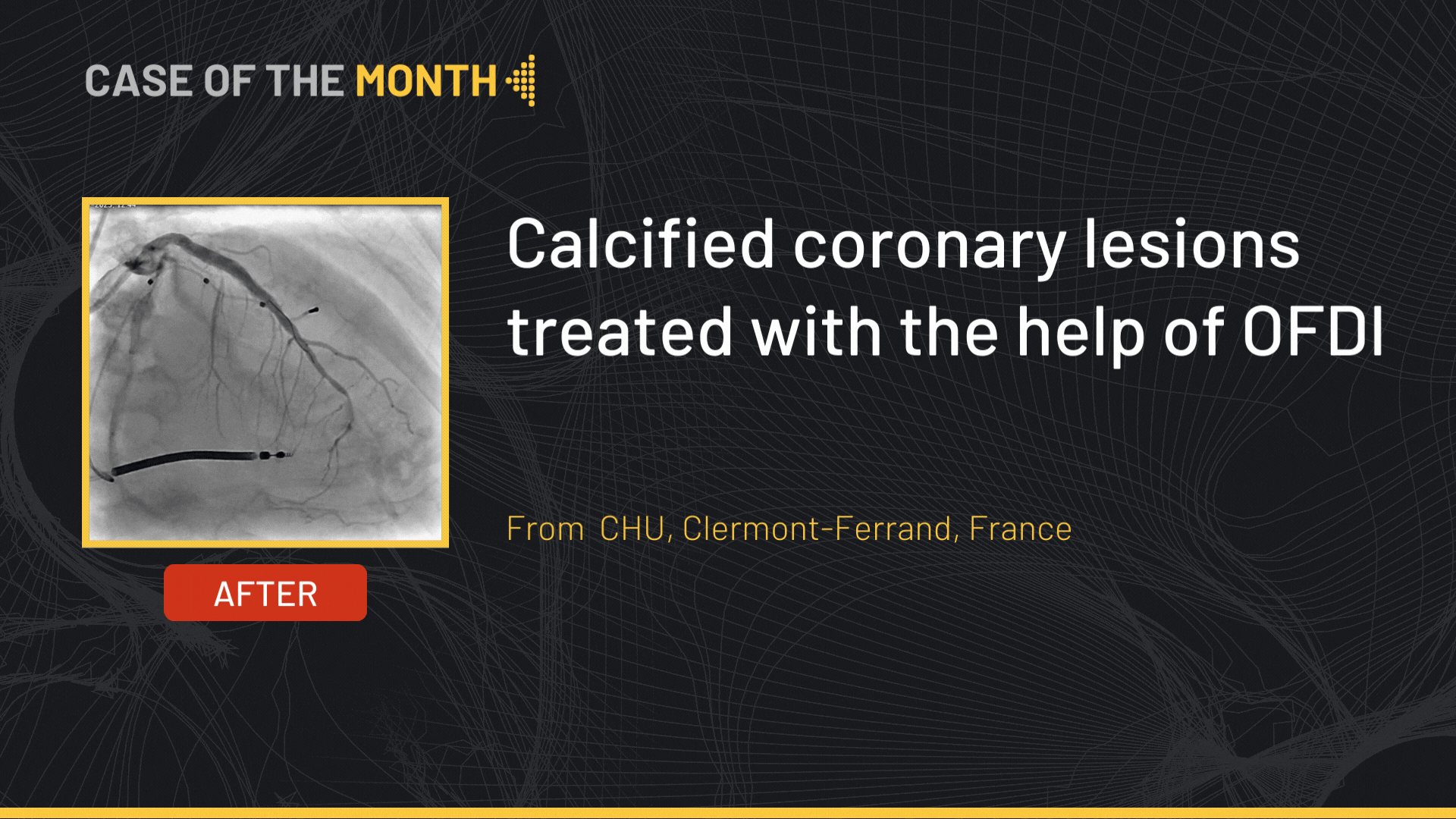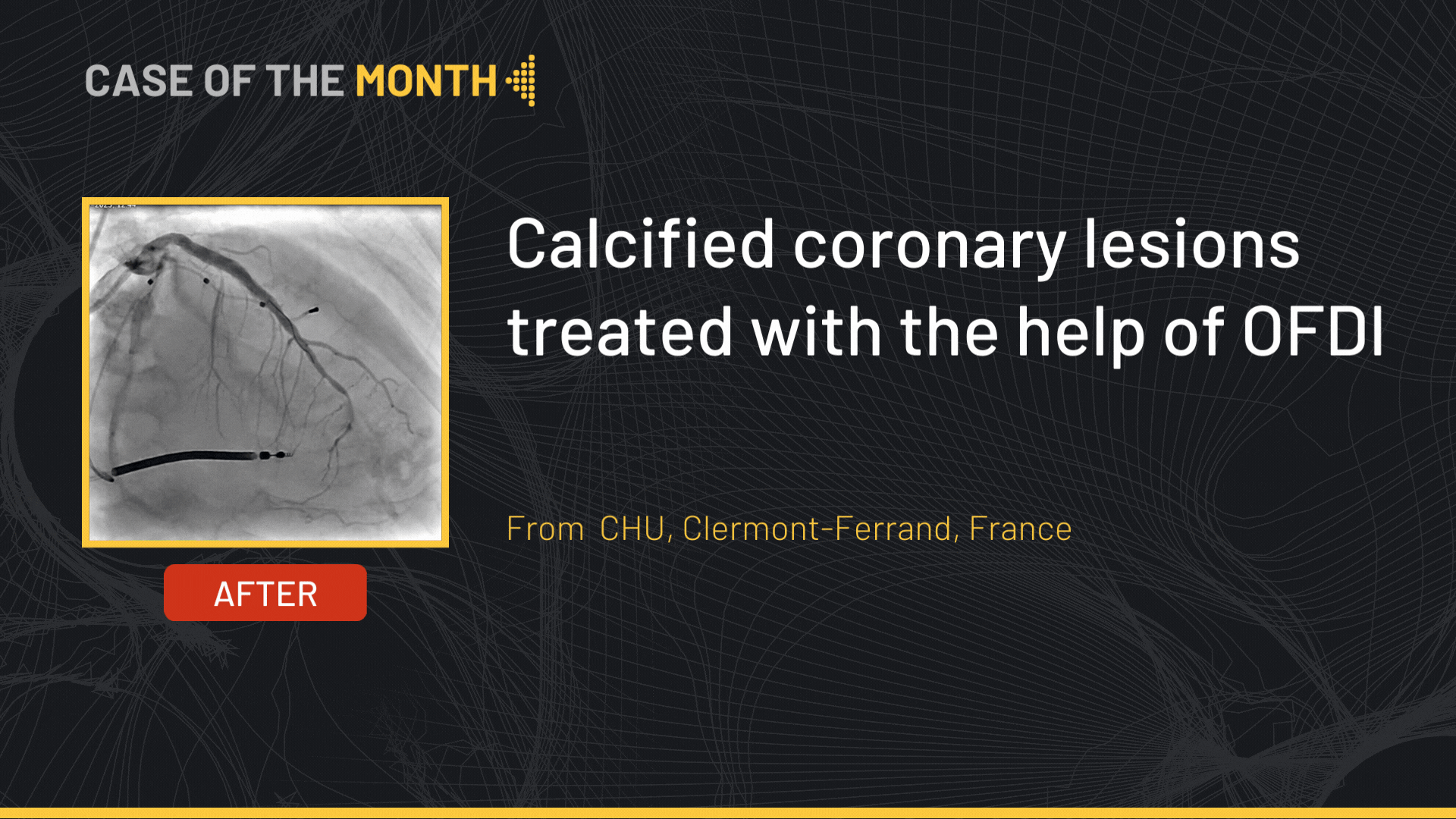
Left CAS for ulcerated Carotid stenosis, Difficult femoral access
Case of the month: June 2021
Partager














Mangesh T. Highly impressed with Proper guidance, Good Selection of Hardware materials, devices used & IR Techniques applied for the Re-Vascularisation of Chronically Occluded (Thrombotic) Left ilio-femoral Venous tract. Cause offcourse May-Thurner’s Compression. Few Questions to Main operator Dr. Houman Jalaie Sir are as follows-
1) Why Atlas gold high pressure balloon used in Post Stenting Dilatation when more pressure is needed in Pre-dilatation and breaking of Chronic fibrotic synaechie in Venous lumen?
2) Mustang has 24 atm bursting pressure while Atlas Gold & Conquest PTA Ballons has 30-40 atm bursting pressure.
3) How Vessel preparation prior to Dedicated Venous Stenting matters more?
4) Can we use Popliteal Vein Access site instead of Mid thigh SFV Site? so that 10 Fr Introducer sheath can be easily fixed and Large bore Stent deployment possible with long working shaft.
5) How aggressively , How long Post Venous Stenting Anticoagulation Therapy followed? What about Surviellence & follow up check ups Schedule in this case?