
Devenez membre d'Incathlab et bénéficiez d'un accès complet !
Inscription Connexion
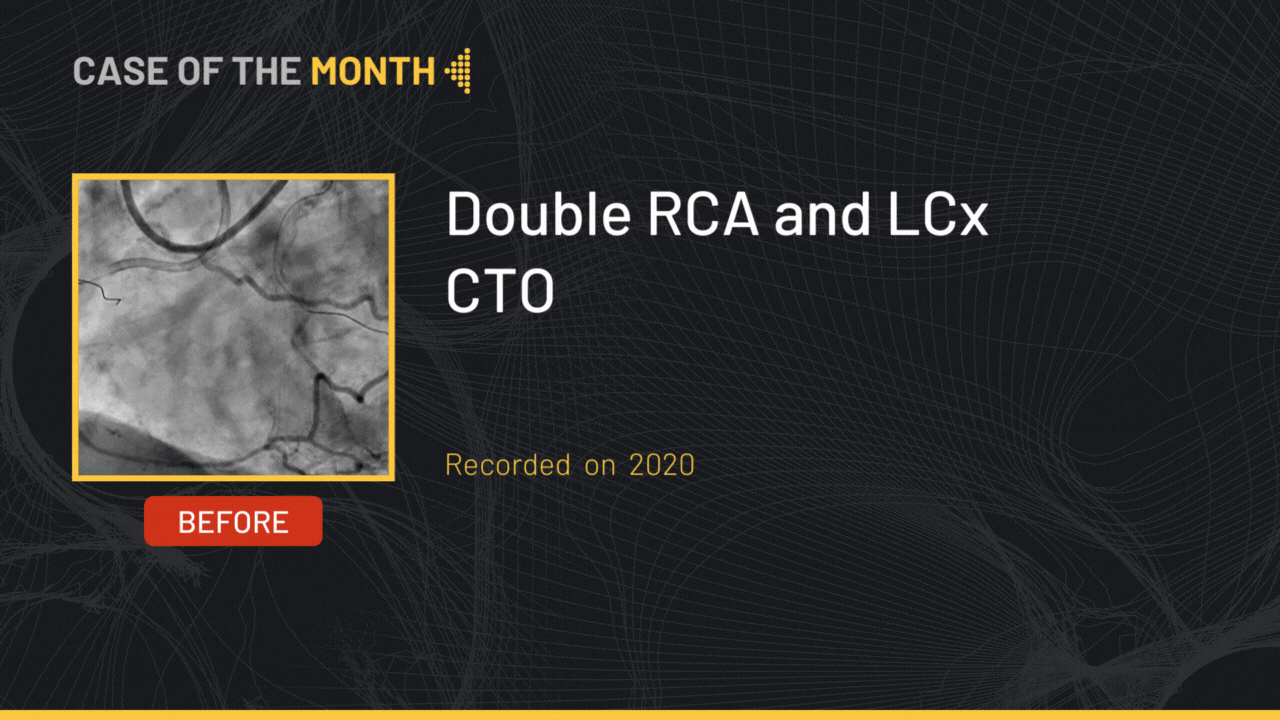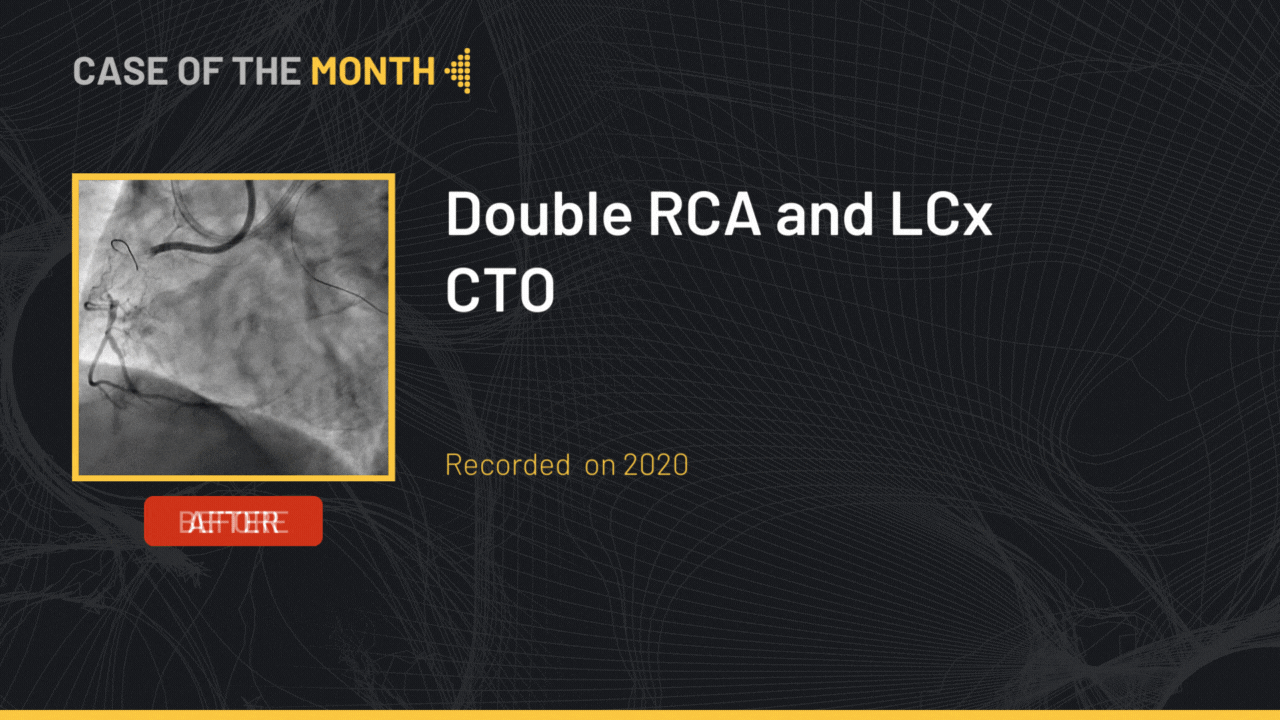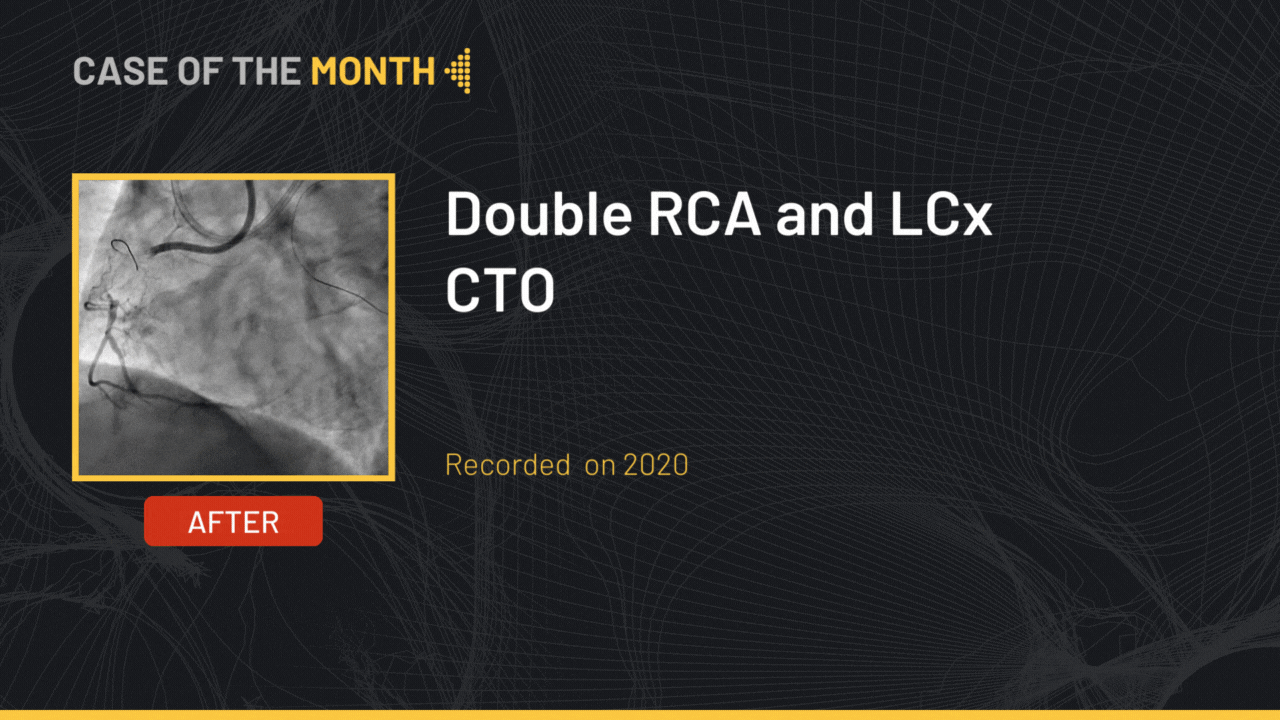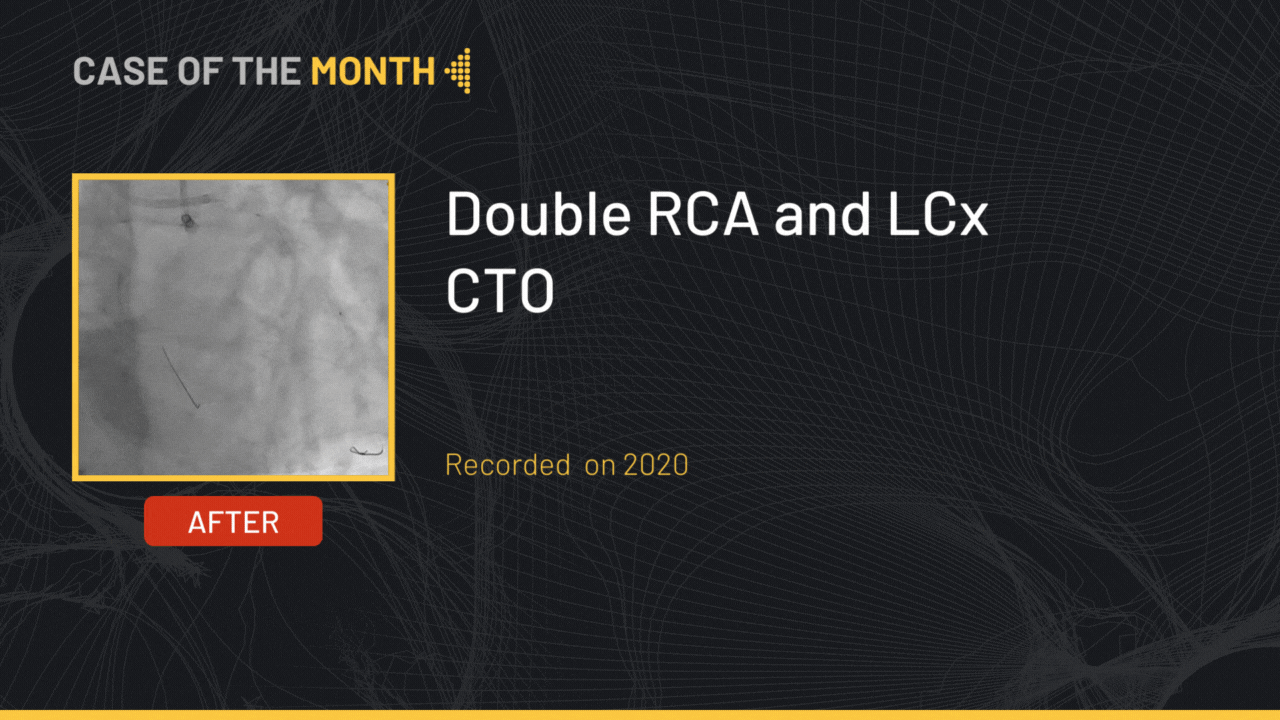
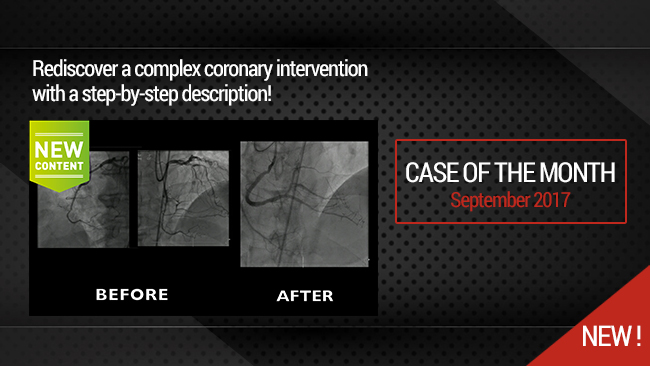
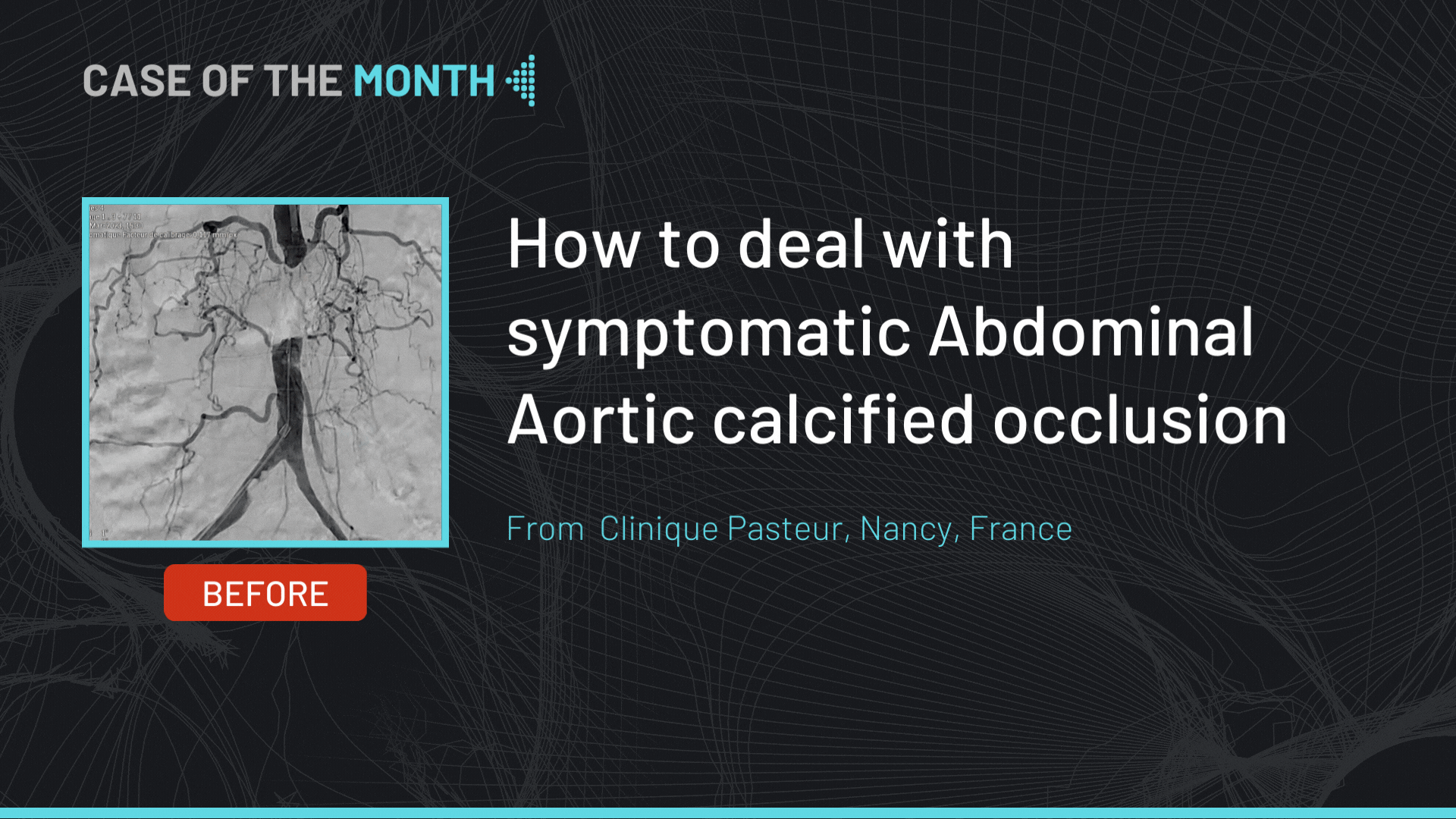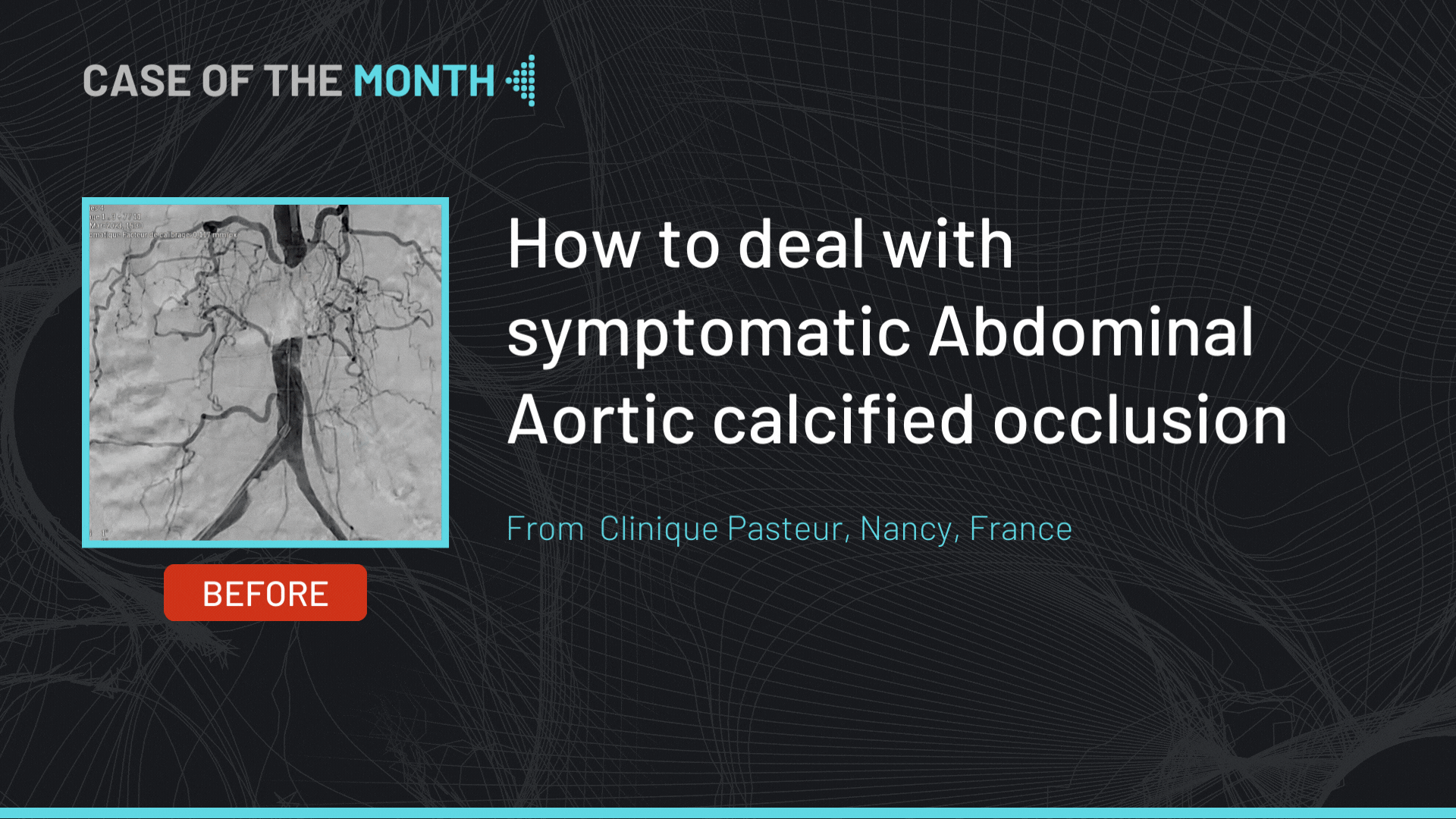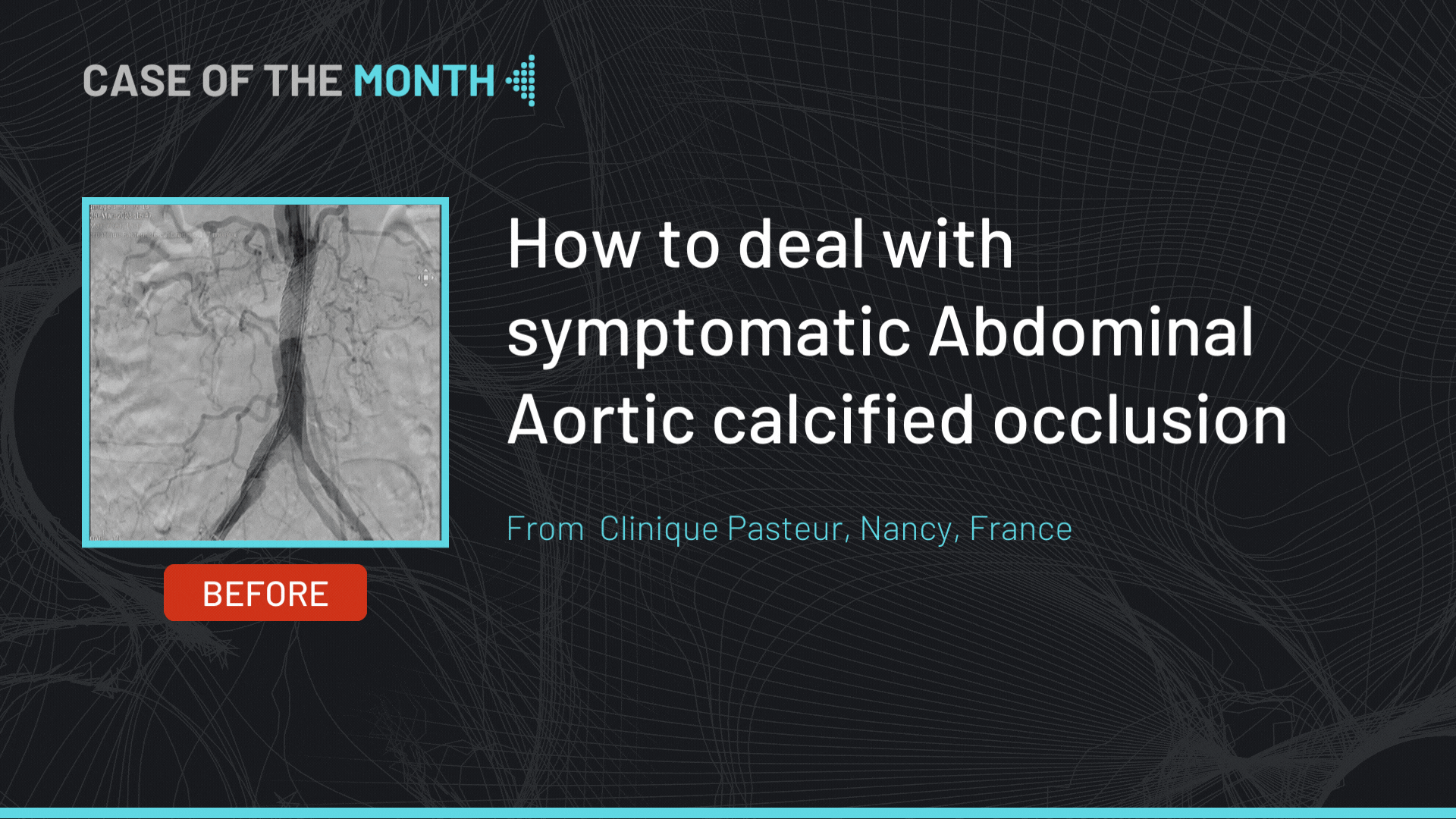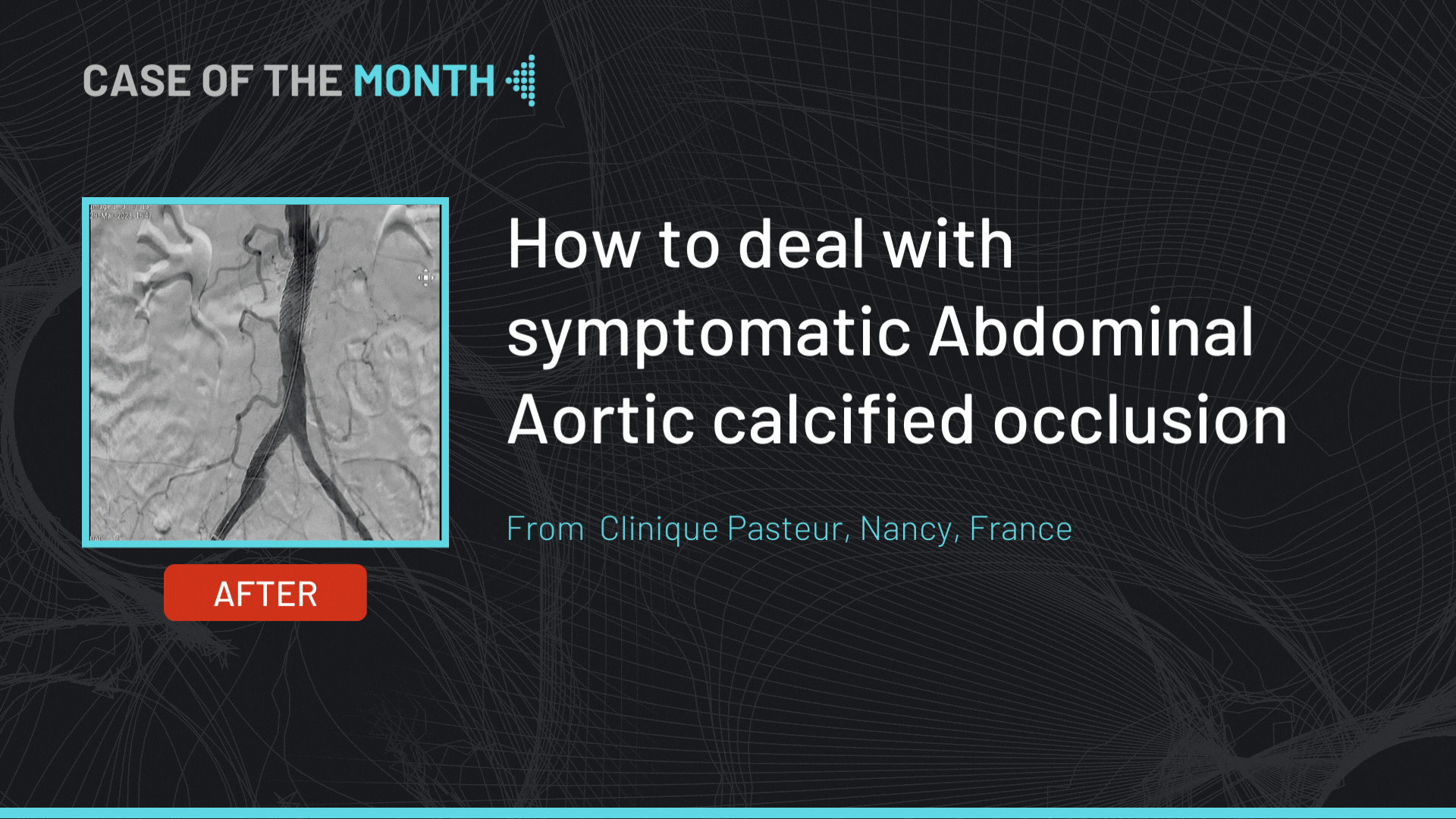
This month, we highlight the case of an RCA and LCx CTO lesion in a 69 years old male patient, s/p STEMI 14 years ago, hypertensive, dyslipidemic and smoker, presenting with dyspnea and worsening LVEF (45 to 35%). Diagnostic coronary angiography showed a CTO of the RCA at the level of the segment 2 presenting an ambiguous proximal cap, longer than 20 mm in length with good distal bed, with bridging collaterals and epicardial collaterals arising from the LAD; no calcifications or bending were noted (J-CTO 2) along with a short CTO of the LCx at the level of the mid segment presenting a tapered proximal cap, with no calcifications and no bending (J-CTO 1). Cardiac MRI showed viability of the inferior and lateral segments.
Educational Objectives
- Plan a step-by-step approach procedure for CTO lesions.
- Antegrade wire escalation.
- Puncture controlled maneuver of the proximal cap.
- Role of IVUS in CTO.
- Assess the viability of retrograde epicardial collaterals.
Step-by-step procedure:
1) Access site:
- Right radial 7Fr sheath: AL 0.75 guiding catheter to the RCA.
- Left radial 7Fr sheath: EBU 4 guiding catheter to the left main.
2) Step by step approach:
The initial strategy for the RCA was antegrade wire escalation along parallel wire technique with ADR as a bail out. The operators will try to avoid a knuckle formation in order to decrease the subintimal space and risk of hematoma.
Using a Samurai guidewire to the marginal branch, an IVUS pullback was performed in order to identify the proximal cap helping in the puncture was not helpful.
Using a Mamba Flex 135 cm microcatheter, a Judo 6 guidewire could not progress through the proximal cap and was changed to a Hornet 14 was able to cross the latter. An IVUS from the marginal branch showed the intraplaque crossing at the proximal cap.
The microcatheter is advanced and the Hornet 14 wire was switched back to Judo 6 that crosses the body of the CTO and finds its way to the distal RCA followed by the microcatheter.
Judo 6 was switched to a Samurai guidewire and pre-dilatation of the body of the CTO using a small 2.0x20 mm semi compliant balloon at 12 atm was performed in order to make room for the IVUS catheter.
An IVUS pullback showed an intraplaque path of the wire as well as a high calcium load.
Pre-dilatation using a 3.0 mm non-compliant balloon was carried out followed by stenting using a Megatron 3.5x38 mm stent according to IVUS measurements.
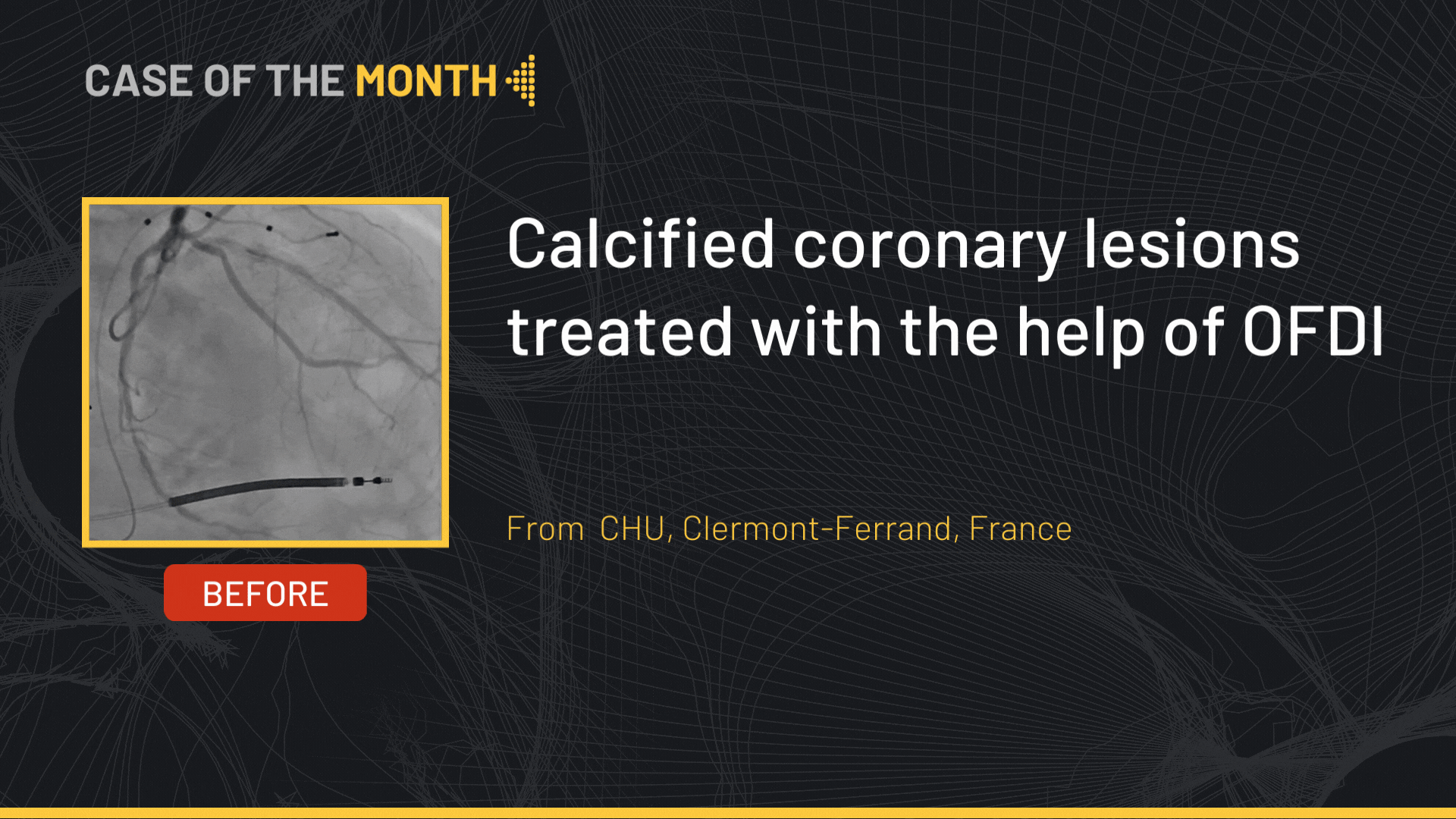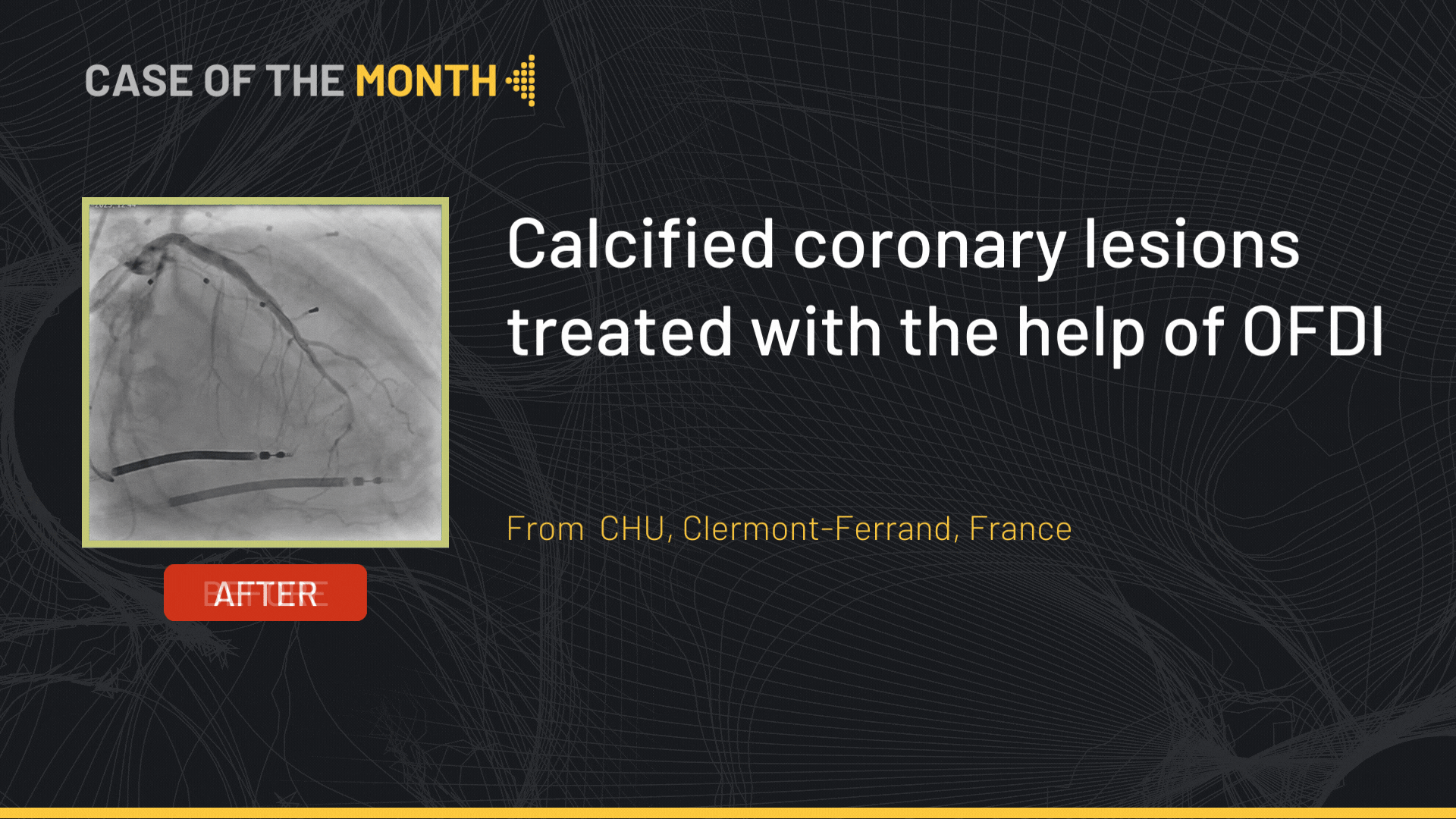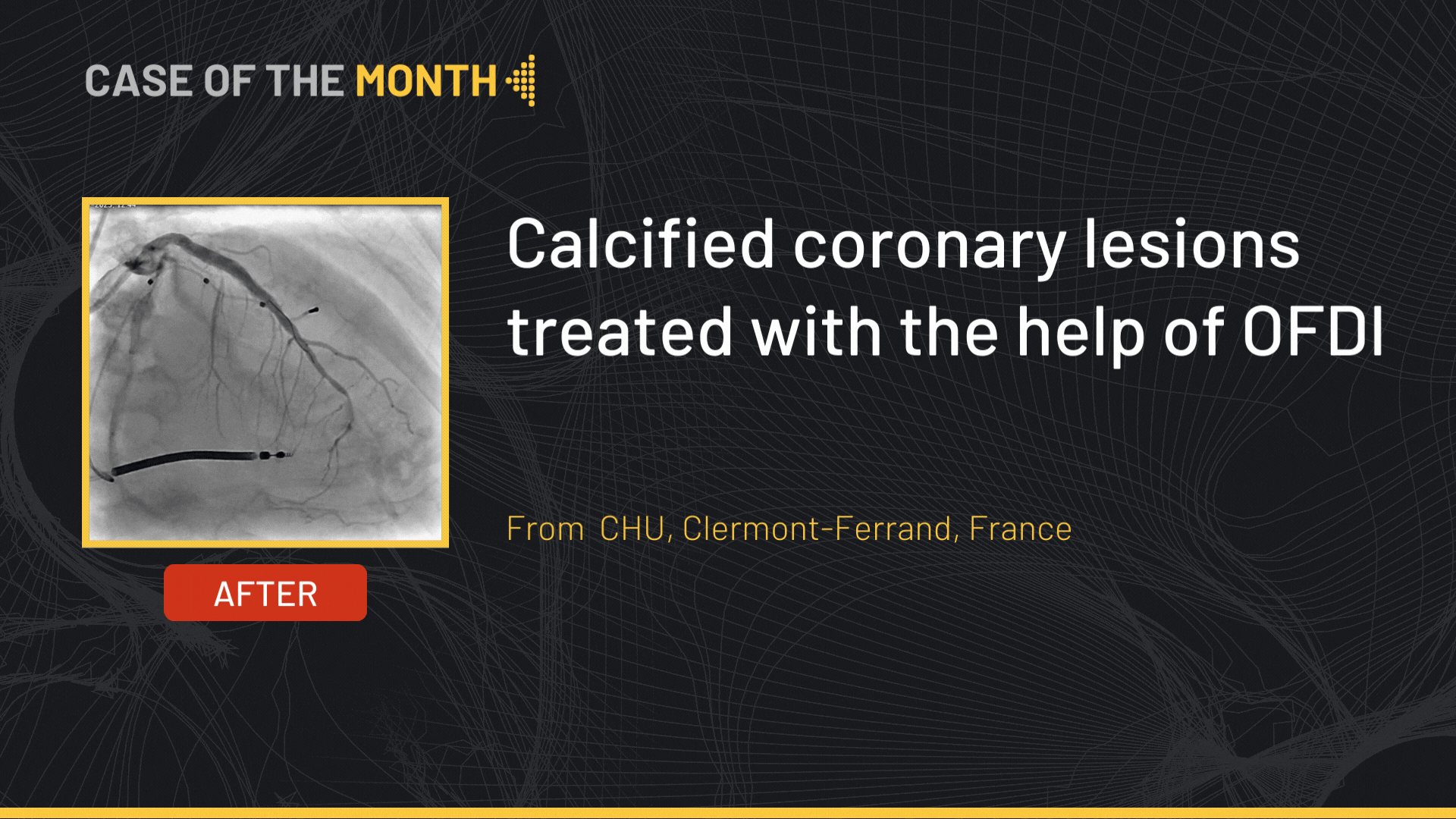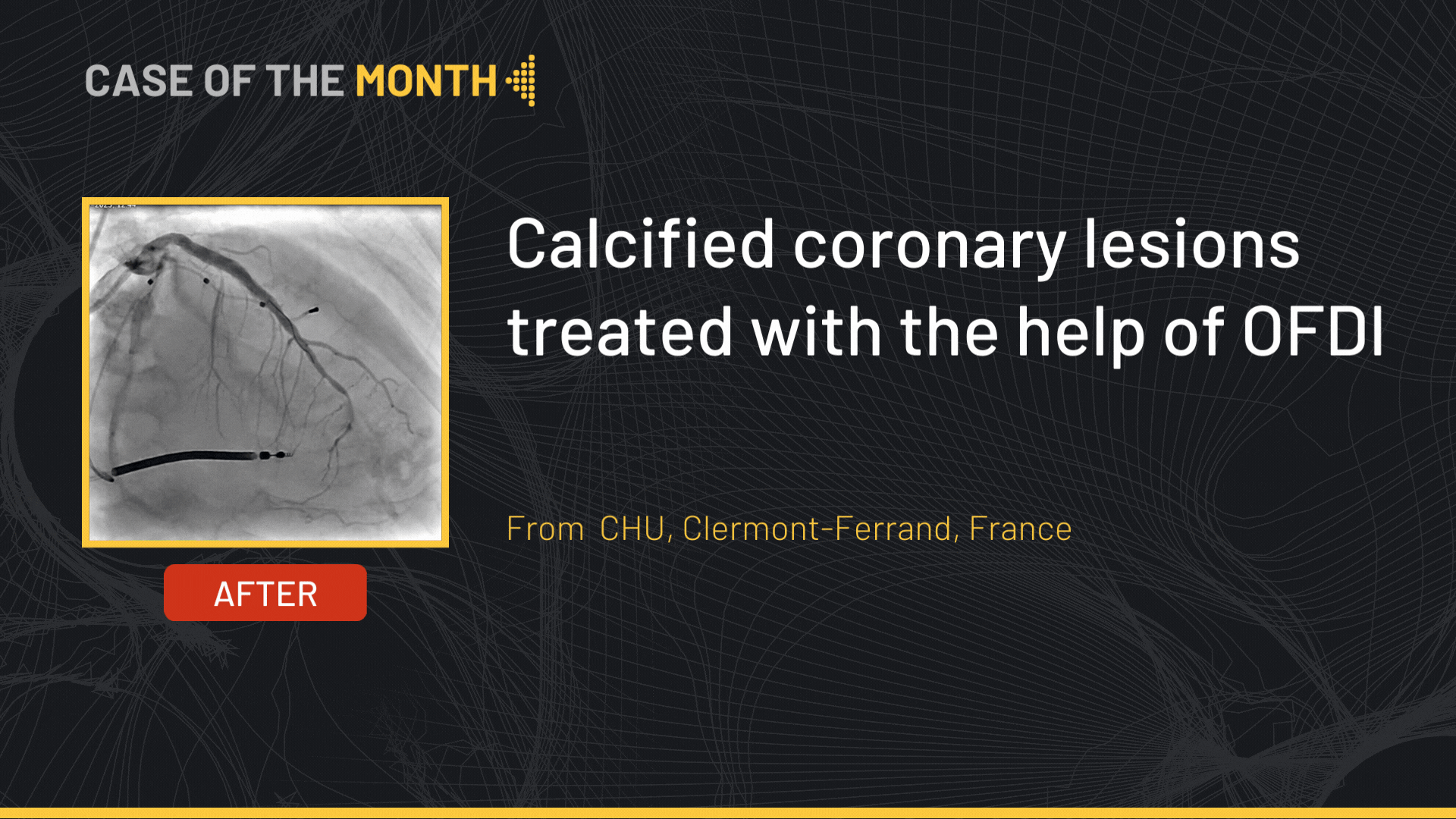
A dissection plane was noted at the proximal RCA that was treated by stenting up to the ostium.
Since a low radiation dose was given, the decision to treat the CTO of the LCx was taken.
Using a Mamba Flex 135 cm microcatheter, a Judo 6 wire was able to find the microchannel and cross the CTO.
Balloon pre-dilatation was carried out followed by an IVUS pullback showing an intraplaque path of the wire.
Stenting of the body of the CTO was carried out using a Synergy 2.75x38 mm followed by post-dilatation using a 3.0 mm non-compliant balloon.
The final angiographic end-result showed a satisfactory result.

Bibliography
Dernière mise à jour : 23/05/2024
Our Cases of the Month
The case of the month is a new way for our users to watch, learn, and share with incathlab. They can watch a video that highlights an innovative case and uses excellent pedagogical techniques, lear...





Gafer A. Hi can I join the discussion
fatih U. Great result.Sometimes ballooning the lateral branch ostium makes the proximal cap and main branch visible .2,0*12 or 15 mm for this case