
Become an Incathlab member and receive full access to its content!
Registration Login
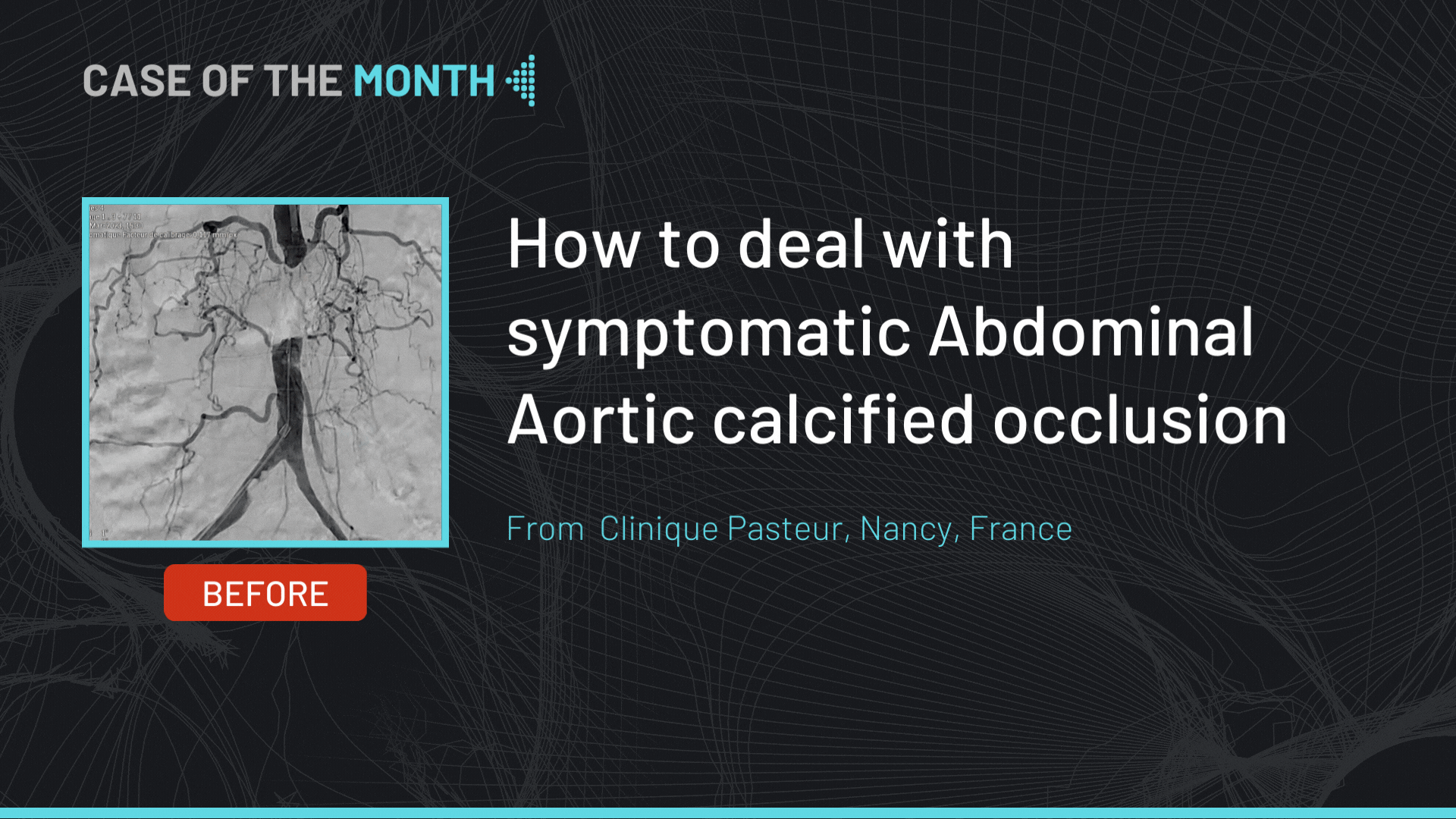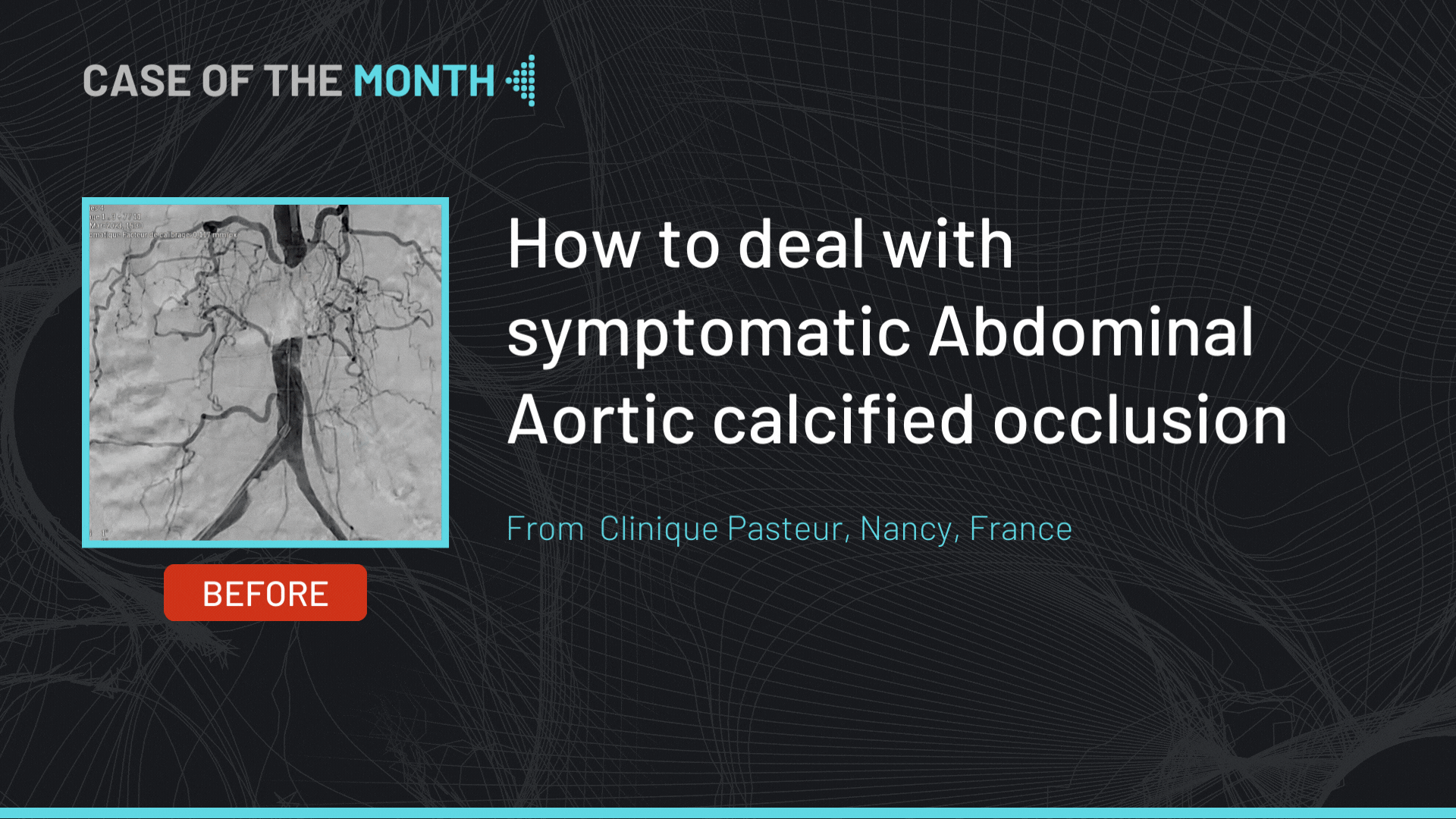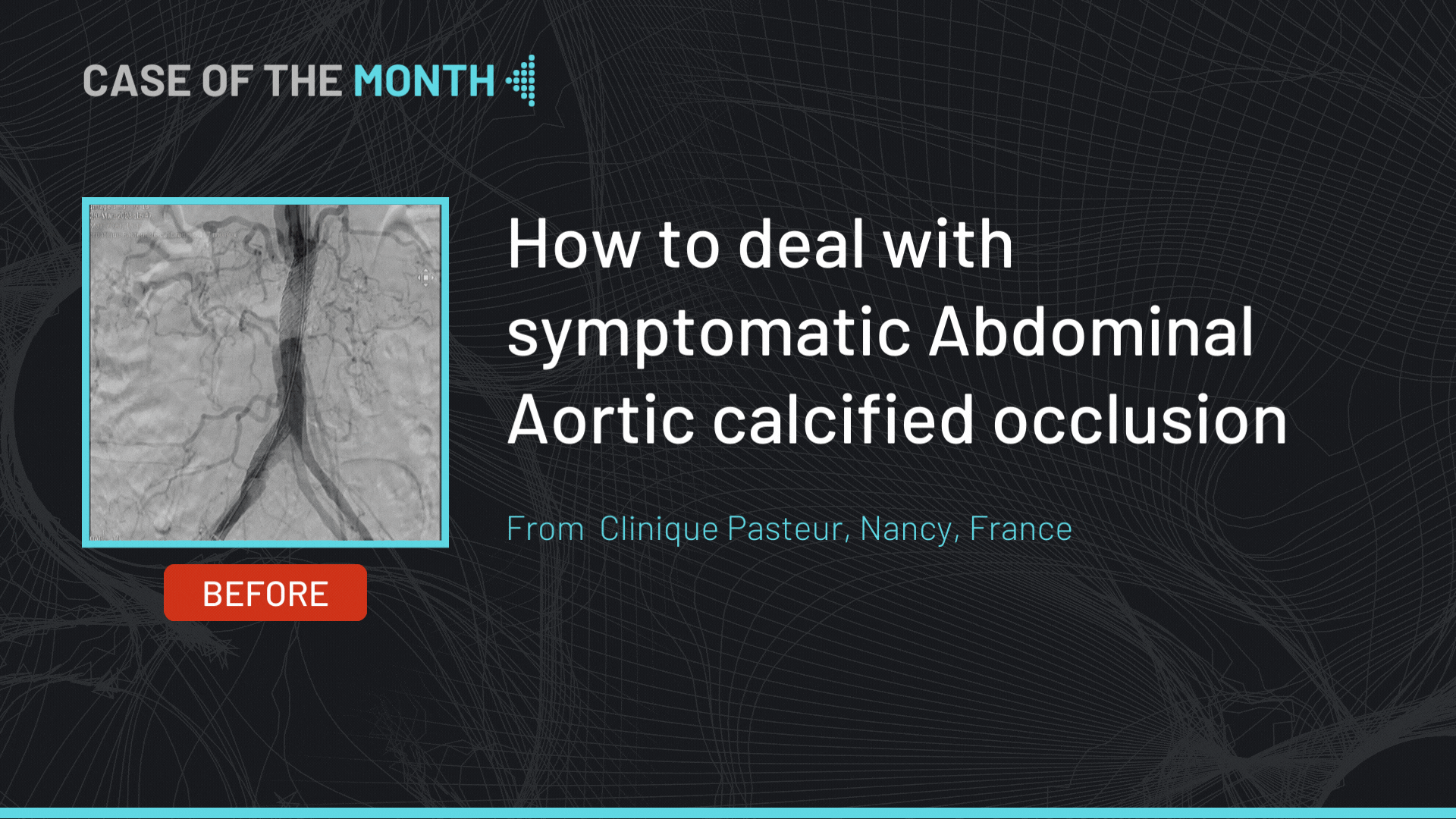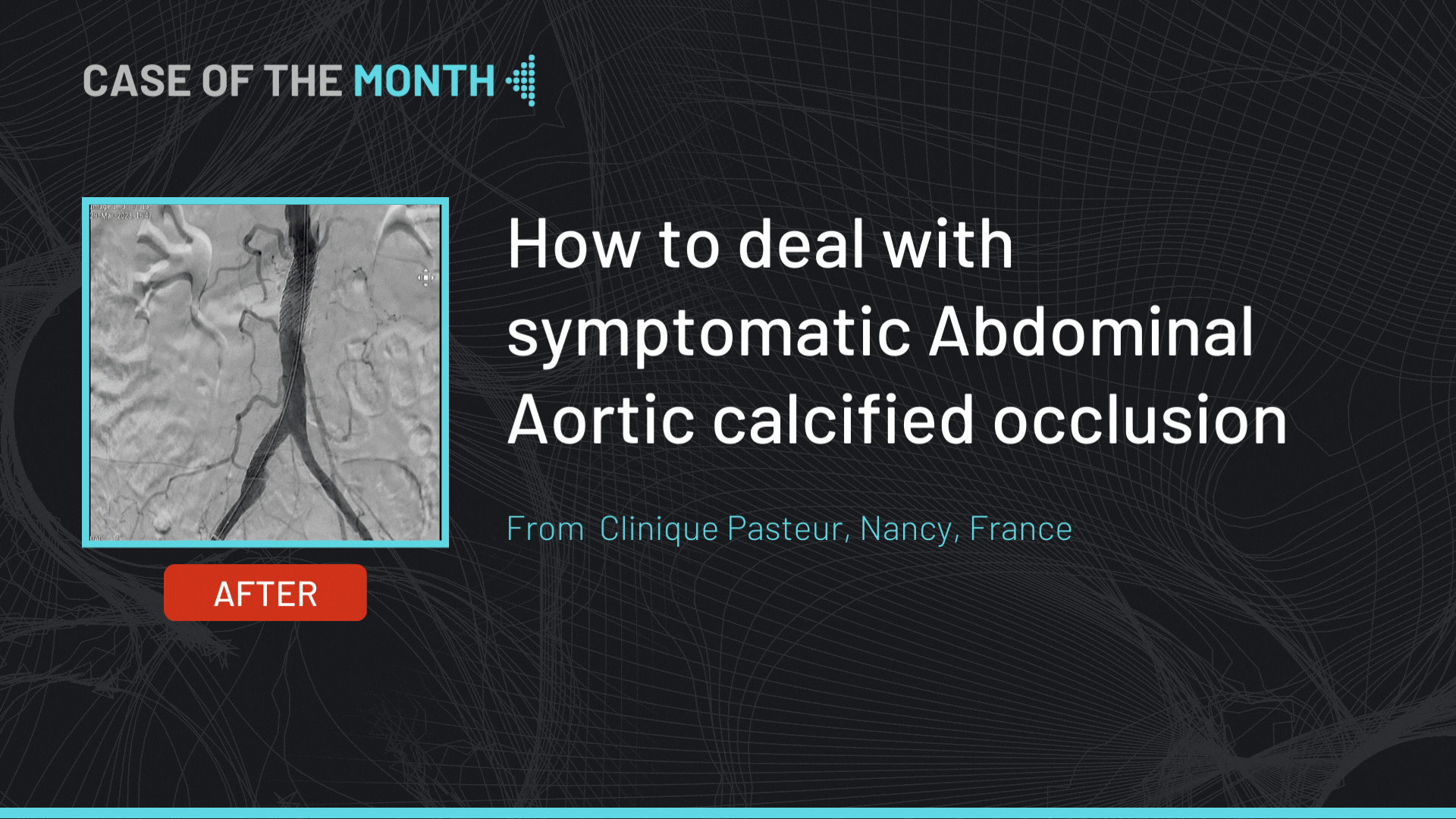
This didactic procedure concerns a 77 years old man with a history of an open replacement of the abdominal aortic aneurysm by bifurcated aorto-bi-iliac graft in 2013, heart failure, atrial fibrillation hypertension and COPD.
He presented to the ER with severe back pain. CT scan showed 70mm diameter thoracic aneurysm with short neck, extended to the abdominal part (coeliac trunk), the infra renal aortic part was replaced in 2013 by open surgery by a bifurcated graft, an occlusion of the left IIA and significant stenosis on both EIA that does not seem to compromise access with the 24 Fr sheath. Both renal arteries and digestive arteries were patents.
Educationnel objectives
- Plan a step-by-step TEVAR procedure.
- How to manage access through challenging anatomy?
- How to proceed to a safe and successful positioning of the endoprosthesis?
- Materials choice.
- Tips and tricks for a good endoprosthesis positioning.
- Endoprosthesis deployment.
Step-by-step procedure:
1) Vascular imaging: CT/angiographic imaging
- Identifying the localization and the extent of the aneurysm.
- Identifying the adjacent vessels that could interfere with the graft position.
- Identifying access challenges: vessel stenosis, tortuosity, anatomy and previous endograft.
2) Vascular access
- 1st access: right femoral access: Gentle navigation and dotterization through the right EIA stenosis, and advance a 24 Fr sheath introducer GORE® DrySeal.
- 2nd access: Left femoral access: 5 Fr sheath; 5 Fr Pigtail for angiography positioned in the aorta. Difficult access through left EIA stenosis and dissection with successful access to the aortic true lumen.
3) Conformable GORE® TAG® Thoracic Endoprosthesis positioning in the thoracic aorta
- Identifying the proximal and distal landing zone: In this case; Proximal landing zone: Distally from the takeoff of the left common carotid artery (just below the takeoff of the left common carotid artery). Distal landing zone: Above the coeliac trunk (1cm above). There is no landing zone distal to the left subclavian artery so it was planned to cover the left subclavian artery: Both vertebral arteries were checked to be patents. The left subclavian artery will be vascularized through the left vertebral artery.
- Careful choice of the right orthogonal view with the least parallax for optimal positioning of the graft.
- Ensure that blood pressure is below 100mmHg.
- Advancement of the Conformable GORE® TAG® Thoracic Endoprosthesis with active control System on a 0.035” Lunderquist® Extra-Stiff Wire through the 24 Fr introducer with gentle navigation through the aorto-bi iliac graft.
- The Tip marker of the endoprosthesis should be oriented to the outer curve.
- Positioning of the endoprosthesis the closest to the takeoff of the left common carotid artery.
- Important remarks to take into consideration while positioning the endoprosthesis: The sleeve of the endograft begins at the top of the first struts and the coverage is at the middle of the first struts, so it’s important to keep the tip of the first struts distal to the common carotid artery. The marker should be at the level of the takeoff of the artery but not more proximal to avoid compromising the patency of the artery.
- Angiographic control of the position of the endoprosthesis.
4) Deployment of the endoprosthesis
- Opening of the endoprosthesis to 50% by turning the grey handle.
- Angiographic control of the deployment and the position of the first struts.
- Adjust the endoprosthesis position up/downstream for an optimal positioning.
- Complete opening of the endoprosthesis from distal to proximal.
- Complete deployment after release the angulation control and the suture.
- Withdraw the introducer
- Angiographic control of the final endoprosthesis position.
5) Deployment of the second and the third endoprosthesis
- Deployment of the second endoprosthesis ensuring a good overlapping.
- Deployment of the third endoprosthesis above the coeliac trunk: distal struts just above 10mm of the takeoff of the coeliac trunk.
- Angiographic control ensure: good position, no type I endoleaks and vessels patency (left and right carotid arteries, left and right vertebral arteries, left subclavian artery through the left vertebral artery and digestive arteries).
- No post-dilatation due to wall thrombus.
6) Vascular closure
7) Clinical observation in CCU for 24h
Protocol
- Procedure time: 75 Min
- Exposure time: 23 min
- Exposure: 2,242 Gy
- Contrast volume: 205 ml ultravist 300 bayer
Bibliography
-
Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR) for the treatment of aortic diseases: a position statement from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), in collaboration with the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Grabenwoger M, Alfonso F, Bachet J, Bonser R, Czerny M, Eggebrecht H, et al. Thoracic. Eur Heart J. 1 juill 2012;33(13):1558‑63.
-
Outcome analysis of the Gore Conformable Thoracic Stent Graft with active control system for the treatment of arch and descending thoracic aortic disease. Böckler D, Bischoff MS, Kronsteiner D, Skrypnik D, Meisenbacher K. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1 déc 2021;60(6):1455‑63.
-
Deployment Accuracy of the Conformable GORE® TAG® Thoracic Endoprosthesis in the Treatment of Zones 2 and 3 Aortic Arch Aneurysms Compared with the Previous TAG®. Ito E, Kanaoka Y, Maeda K, Ohta H, Ishida A, Ohki T. Ann Vasc Dis. 2015;8(2):74‑8.
-
Early and Long-term Results of ePTFE (Gore TAG®) versus Dacron (Relay Plus® Bolton) Grafts in Thoracic Endovascular Aneurysm Repair. Mezzetto L, Scorsone L, Silingardi R, Gennai S, Leone N, Piffaretti G, et al. Ann Vasc Surg. févr 2021;71:419‑27.
-
Evaluation of the Gore TAG thoracic branch endoprosthesis in the treatment of proximal descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. Dake MD, Fischbein MP, Bavaria JE, Desai ND, Oderich G, Singh MJ, et al. J Vasc Surg. nov 2021;74(5):1483-1490.e2.
-
Long-term results of endovascular repair for descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. Ranney DN, Cox ML, Yerokun BA, Benrashid E, McCann RL, Hughes GC. J Vasc Surg. févr 2018;67(2):363‑8.
-
TEVAR: Endovascular Repair of the Thoracic Aorta. Nation D, Wang G. Semin Interv Radiol. 18 août 2015;32(03):265‑71.
-
The GORE TAG conformable thoracic stent graft with the new ACTIVE CONTROL deployment system. Mariani C, van der Weijde E, Smith T, Smeenk HG, Vos JA, Heijmen RH. J Vasc Surg. août 2019;70(2):432‑7.
Last update : 2022-03-21
Our Cases of the Month
The case of the month is a new way for our users to watch, learn, and share with incathlab. They can watch a video that highlights an innovative case and uses excellent pedagogical techniques, lear...







Adnan J. Very nice case thanks