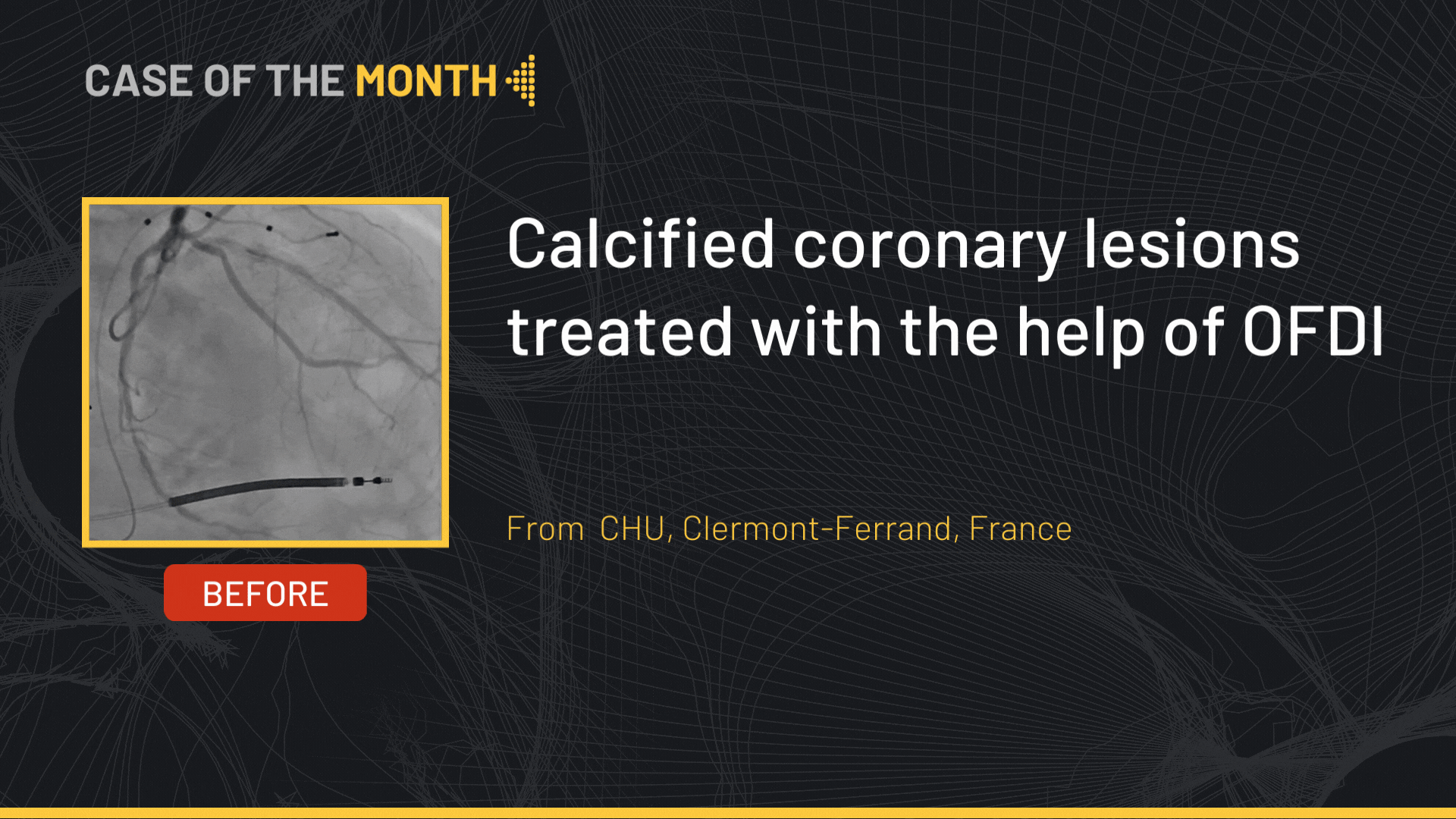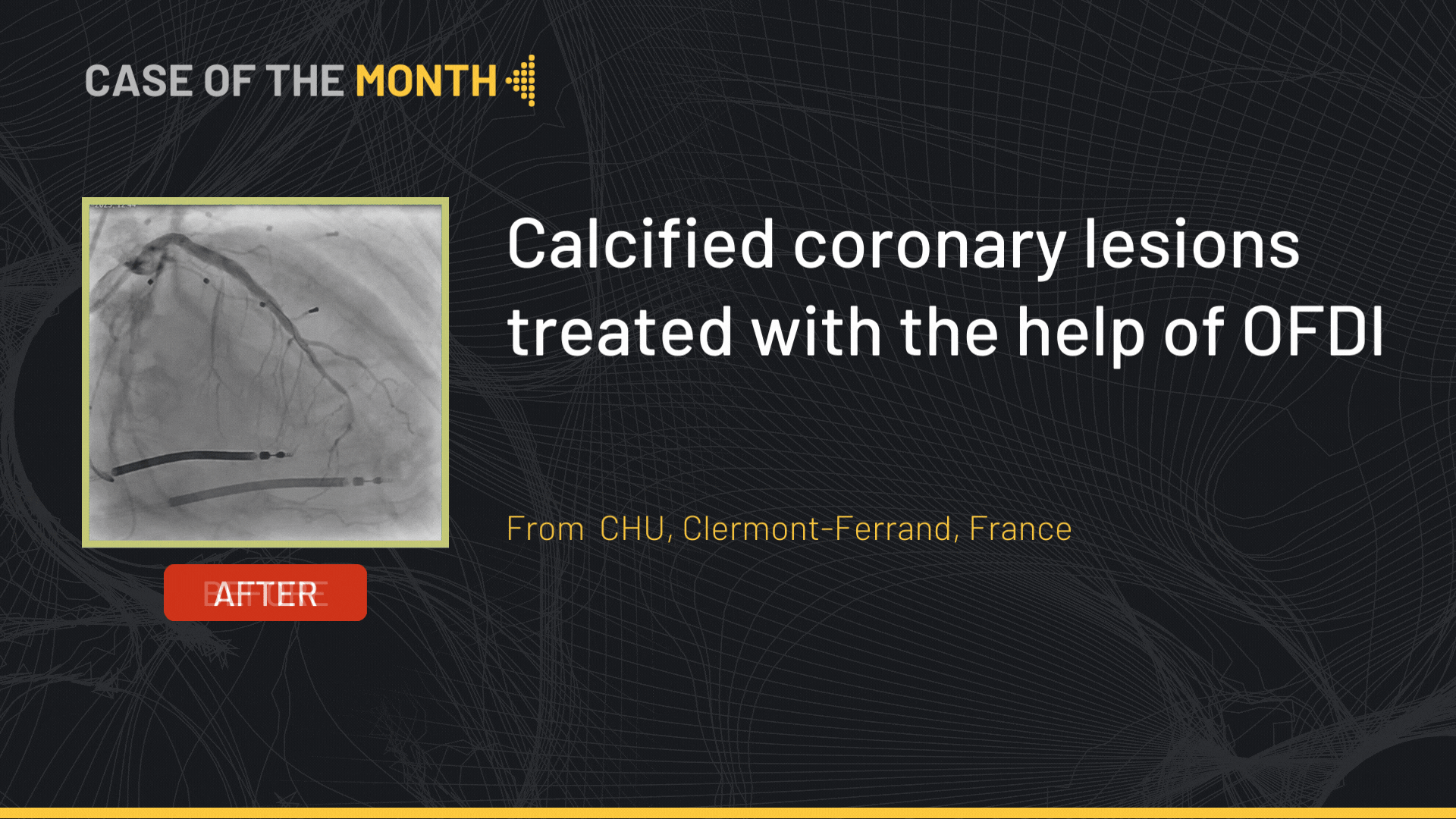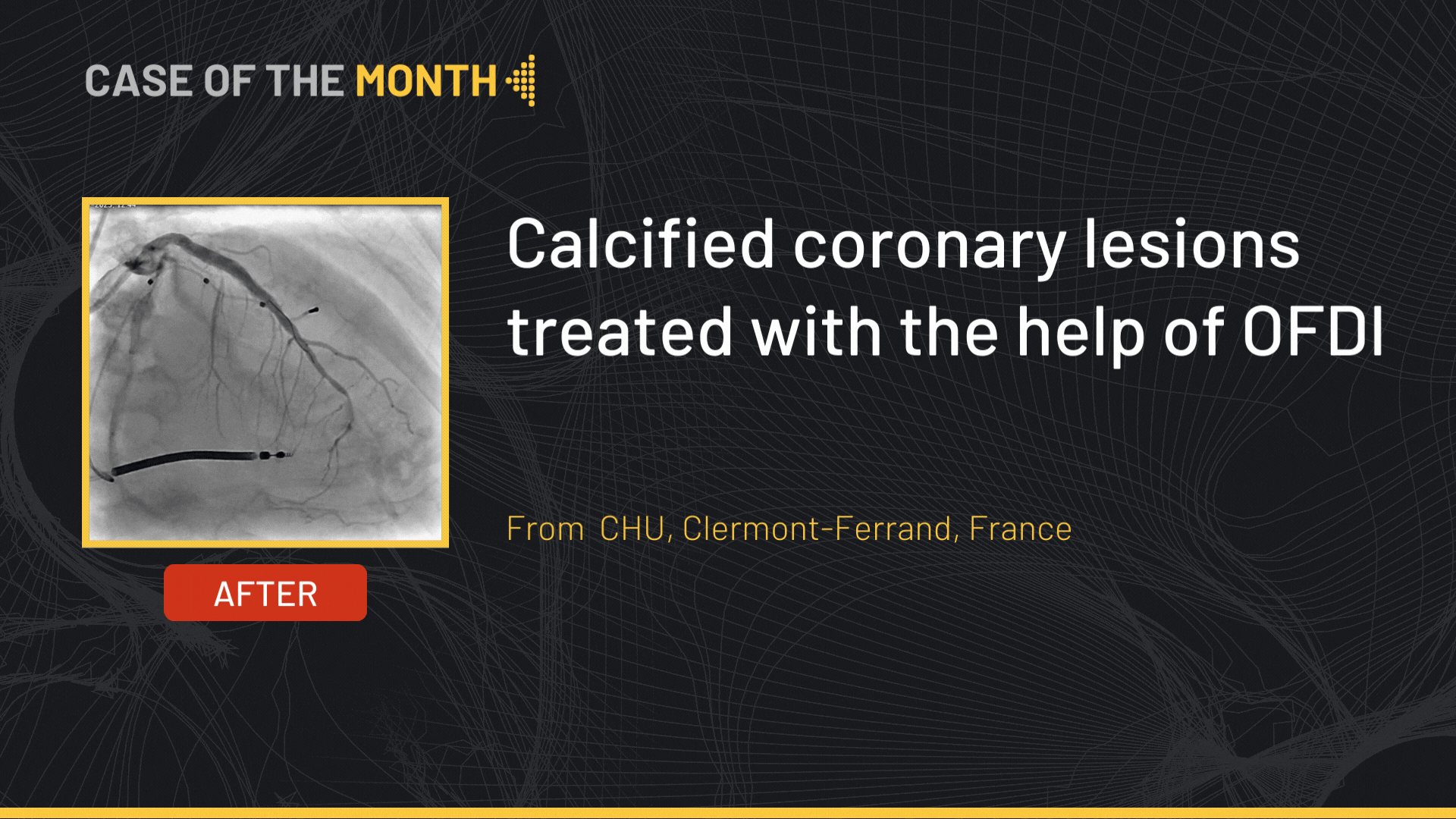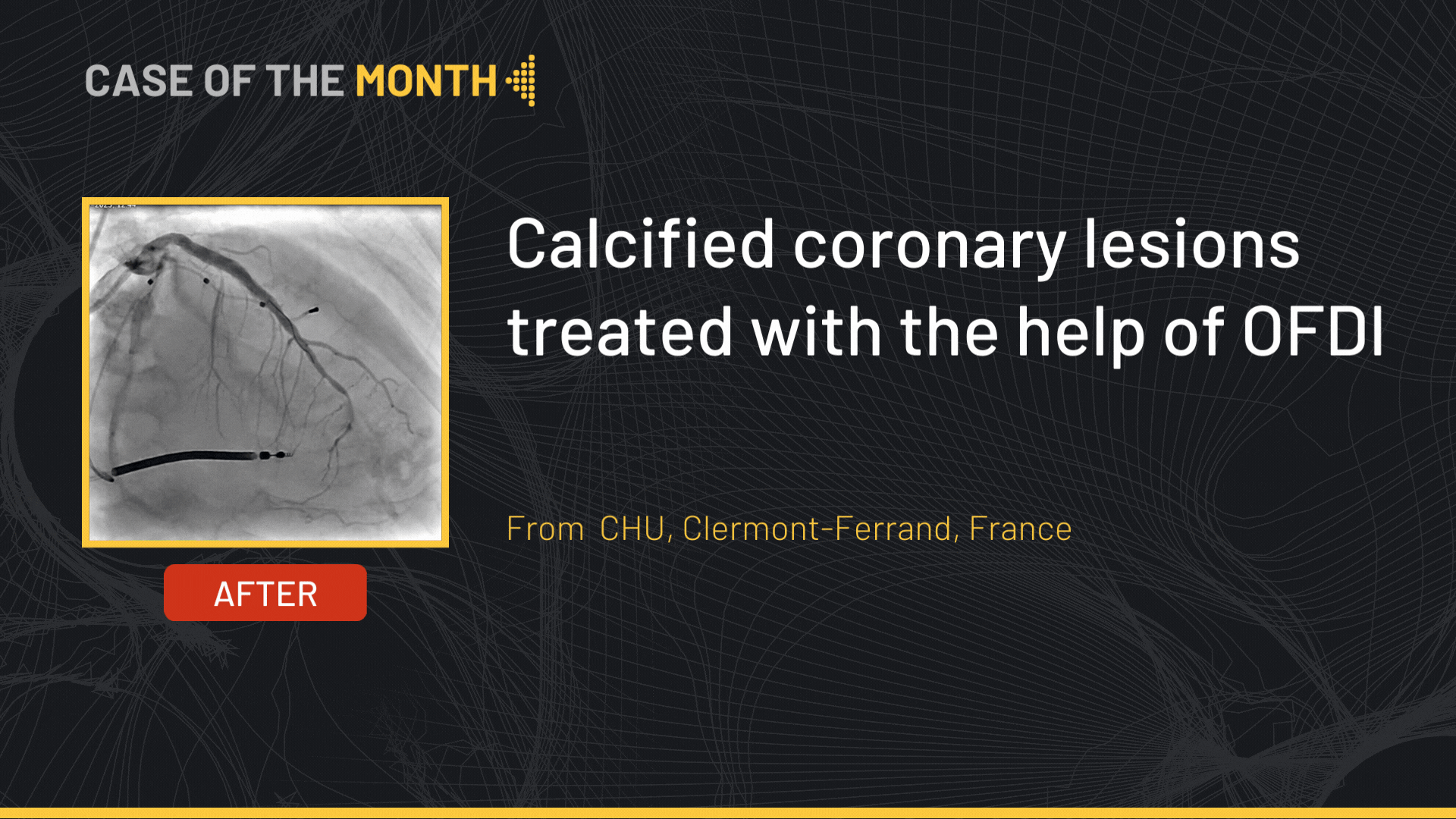
This didactic procedure concerns a 66 years old women presenting bilateral intermittent claudication, Past history: Endarterectomy of left internal carotid artery in 2014.
Global angiography revealed: Firstly, Two Vessels Coronary lesions, Secondly bilateral common femoral severe calcified stenosis, Thirdly Restenosis post endarterectomy of left internal carotid, De novo Right internal carotid stenosis, and occlusion of right brachiocephalic trunk, and occlusion of left subclavian artery.
The first procedure involved recanalization of the subclavian artery with a covered Stent BENTLEY® followed by bilateral Shockwave of Left and Right common femoral arteries and final deployment Supera Stent ®
The Second procedure that we show here consisted of Right intern carotid artery stenting and Brachiocephalic trunk recanalization.
Dual antiplatelet therapy before the procedure and Interruption of anti-hypertensive therapy the day before.
Educational objectives
- How to manage multivascular patient with multiple lesion location: In what order should these different lesions be treated and by which approach?
- Plan a step-by-step carotid artery and brachiocephalic trunk stenting procedure.
- How to manage access through tortuous anatomy? Brachial or Femoral approach?
- How to proceed to a safe and successful catheterization of the right internal carotid artery and brachiocephalic trunk?
- Materials choice: guidewires, protection filter, guiding catheter, balloons and carotid stent.
- How to prepare, advance the embolic protection system: FilterWire EZ™ through the lesion and release the filter upstream the lesion?
- Tips and tricks for a good positioning and implantation of the Micro Mesh carotid stent.
- How to safely retrieve the embolic protection system: FilterWire EZ™?
- What are adjunctive per procedural pharmacotherapies.
Step-by-step procedure: Right internal carotid artery stenting
1) Access sites:
- Brachial approach : 6 French braided introducer sheath
- Femoral access: 8 French access using micro puncture system.
- Heparin administration.
2) Right common carotid artery catheterization:
- Continuous flushing of the guiding catheter while introducing guidewire, embolic protection device, balloons or stent.
- Advance softly an 6 Fr PENUMBRA Guiding catheter to the subclavian artery over a 0.035’’ Stiff GUIDEWIRE
- Advance the 0.035” Guidewire towards the common carotid artery.
- Switching to 0.035” ADVANTAGE Terumo ® Wire then to AMPLATZ wire in order to have more support
- Advance the selective guiding catheter and the 6 Fr PENUMBRA introducer to the distal part of the common carotid artery with the tip oriented towards the internal carotid ostium.
3) Preparation and deployment of embolic protection system: FilterWire EZ™:
- Preparation of the filter with a special attention to avoid air bubbles.
- Preform the wire tip shape according to the lesion morphology.
- Careful and gentle crossing of the lesion avoiding plaque destabilization.
- Release the filter in a vertical segment of the internal carotid distally to the lesion: be sure to have enough space for stent distal landing zone.
- Verify the good position and the opening of the filter under fluoroscopy.
4) Pre-dilatation
- Atropine administration
- Good balloon preparation: avoid air bubbles to avoid cerebral air embolism in case of balloon rupture.
- Pre dilatation of the lesion using a 4 x 30mm Ultra-Soft™ balloon , inflated to 4 ATM
- Checking pre dilatation result , no more backflow after predilatation
5) Stenting
- Select the precise spot of stent deployment
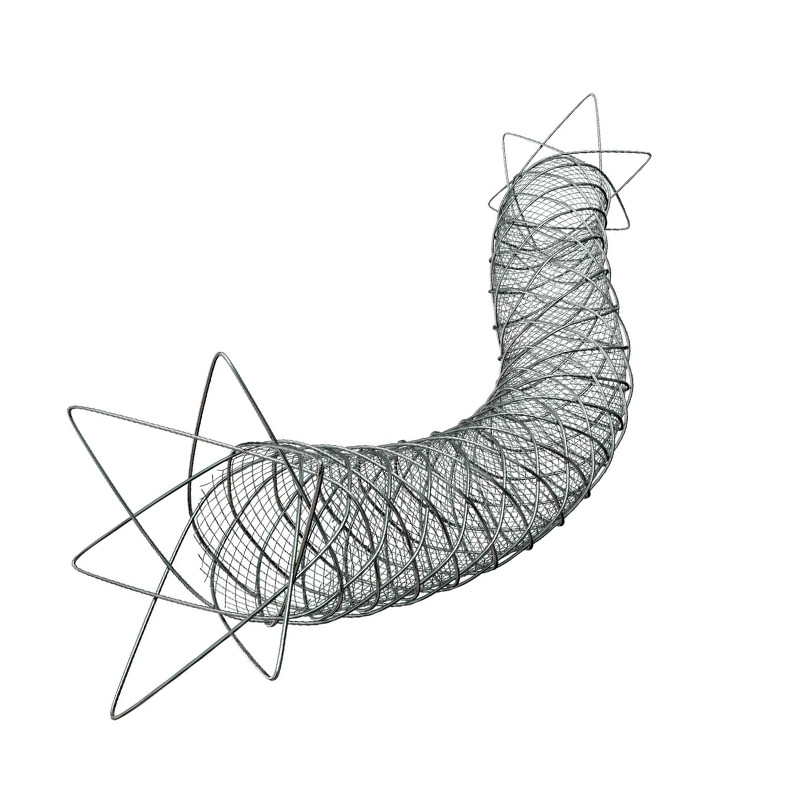
- Deployment of the ROADSAVER micromesh stent terumo ® 8 x 20 mm
6) Post-dilatation
- Post dilatation of the lesion using a 5 *15 mm Ultra-Soft™ balloon. Inflated to 15 ATM
- Checking post dilatation result.
7) Retrieval of embolic protection system: FilterWire EZ™:
- Check the filter content and the quality of the flow.
- Remove the filter.
- Verify if there is any dissection or spasm.
8) Final angiographic control: Cervical and Intra-cranial ( 2 views Frontal & Lateral)
Step-by-step procedure: Brachiocephalic trunk stenting
1) Access sites:
- Brachial approach: 6 French introducer sheath
- Femoral access: 8 French access using micro puncture system.
2) Brachiocephalic trunk artery catheterization:
- Braided Femoral Introducer Sheath 7 French 70 cm crossed gently the Femoral Stent Supera OD ® , and gently placed in the entrance of brachiocephalic trunk
3) Crossing the lesion :
- Using Asahi Halberd® guidewire 0014 via femoral access before switching to Abbott Spartacore ® 0014 guidewire.
- Advance the Abbott Spartacore ® 0014 guidewire towards the common carotid artery in order to have more support.
- Use of the BER II catheter to steer another Abbott Spartacore ® 0014 guide wire to the subclavian artery.
4) Pre-dilatation
- We change to a 0035 guide wire to have more support before predilatation
- Predilatation toward the subclavian artery using 6 x 60 mm Shockwave balloon
5) Stenting brachiocephalic trunk
- Stenting toward the subclavian artery with : Bentley covered stent ® 8X37 mm
- Using caudal view in order to place the stent in the level of the carina between common carotid and the subclavian artery
6) Final angiographic control: Verify if there is any dissection or spasm.
Medical adjunctive treatments
- Pre-procedural: Heparin.
- During procedure : Atropine and ephedrine.
- Post procedural : double therapy: Aspirin 75mg o.d. + Clopidogrel 75mg o.d for one month.
- After one month : Scheduling Coronary PCI.
Bibliography
Last update : 2024-01-15
Our Cases of the Month
The case of the month is a new way for our users to watch, learn, and share with incathlab. They can watch a video that highlights an innovative case and uses excellent pedagogical techniques, lear...
Suggestions
San Francisco : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 08am to 09:30am (GMT+1)
New York : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 11am to 12:30pm (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 01pm to 02:30pm (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 04pm to 05:30pm (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 05pm to 06:30pm (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 06pm to 07:30pm (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 08pm to 09:30pm (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Tuesday, March 26th 2024 from 11pm to 12:30am (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Wednesday, March 27th 2024 from 12am to 01:30am (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Wednesday, March 27th 2024 from 01am to 02:30am (GMT+1)
Sydney : Wednesday, March 27th 2024 from 02am to 03:30am (GMT+1)
Wellington : Wednesday, March 27th 2024 from 04am to 05:30am (GMT+1)
CAS e-Contest Final Results
an interactive european contest on carotid artery stenting
San Francisco : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 07am to 08am (GMT+1)
New York : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 10am to 11am (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 12pm to 01pm (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 03pm to 04pm (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 04pm to 05pm (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 05pm to 06pm (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 07pm to 08pm (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 10pm to 11pm (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Monday, February 10th 2025 from 11pm to 12am (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 12am to 01am (GMT+1)
Sydney : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 01am to 02am (GMT+1)
Wellington : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 03am to 04am (GMT+1)
Benefits of braided micromesh
Roadsaver TM Insights Week: Celebrating a Decade of CAS Advances
San Francisco : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 07am to 08am (GMT+1)
New York : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 10am to 11am (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 12pm to 01pm (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 03pm to 04pm (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 04pm to 05pm (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 05pm to 06pm (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 07pm to 08pm (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 10pm to 11pm (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Tuesday, February 11th 2025 from 11pm to 12am (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 12am to 01am (GMT+1)
Sydney : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 01am to 02am (GMT+1)
Wellington : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 03am to 04am (GMT+1)
Radial approach benefits in CAS
Roadsaver TM Insights Week: Celebrating a Decade of CAS Advances
San Francisco : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 07am to 08am (GMT+1)
New York : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 10am to 11am (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 12pm to 01pm (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 03pm to 04pm (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 04pm to 05pm (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 05pm to 06pm (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 07pm to 08pm (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 10pm to 11pm (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Wednesday, February 12th 2025 from 11pm to 12am (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 12am to 01am (GMT+1)
Sydney : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 01am to 02am (GMT+1)
Wellington : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 03am to 04am (GMT+1)
Complex CAS handling
Roadsaver TM Insights Week: Celebrating a Decade of CAS Advances
San Francisco : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 07am to 08am (GMT+1)
New York : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 10am to 11am (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 12pm to 01pm (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 03pm to 04pm (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 04pm to 05pm (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 05pm to 06pm (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 07pm to 08pm (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 10pm to 11pm (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Thursday, February 13th 2025 from 11pm to 12am (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 12am to 01am (GMT+1)
Sydney : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 01am to 02am (GMT+1)
Wellington : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 03am to 04am (GMT+1)
CAS procedural optimization
Roadsaver TM Insights Week: Celebrating a Decade of CAS Advances
San Francisco : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 07am to 08am (GMT+1)
New York : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 10am to 11am (GMT+1)
Buenos Aires : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 12pm to 01pm (GMT+1)
London / Dublin : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 03pm to 04pm (GMT+1)
Paris / Berlin : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 04pm to 05pm (GMT+1)
Istanbul : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 05pm to 06pm (GMT+1)
Moscou / Dubaï : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 07pm to 08pm (GMT+1)
Bangkok : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 10pm to 11pm (GMT+1)
Shanghai : Friday, February 14th 2025 from 11pm to 12am (GMT+1)
Tokyo : Saturday, February 15th 2025 from 12am to 01am (GMT+1)
Sydney : Saturday, February 15th 2025 from 01am to 02am (GMT+1)
Wellington : Saturday, February 15th 2025 from 03am to 04am (GMT+1)
CAS, vascular surgeons' perspective
Roadsaver TM Insights Week: Celebrating a Decade of CAS Advances
San Francisco : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 08am to 09:30am (GMT+2)
New York : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 11am to 12:30pm (GMT+2)
Buenos Aires : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 12pm to 01:30pm (GMT+2)
Reykjavik : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 03pm to 04:30pm (GMT+2)
London / Dublin : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 04pm to 05:30pm (GMT+2)
Paris / Berlin : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 05pm to 06:30pm (GMT+2)
Istanbul : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 06pm to 07:30pm (GMT+2)
Moscou / Dubaï : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 07pm to 08:30pm (GMT+2)
Bangkok : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 10pm to 11:30pm (GMT+2)
Shanghai : Thursday, June 22nd 2023 from 11pm to 12:30am (GMT+2)
Tokyo : Friday, June 23rd 2023 from 12am to 01:30am (GMT+2)
Sydney : Friday, June 23rd 2023 from 02am to 03:30am (GMT+2)
Wellington : Friday, June 23rd 2023 from 04am to 05:30am (GMT+2)